Taking control of your finances can be daunting, especially if you’re just starting out. But don’t worry, it’s never too early (or too late!) to learn the basics of personal finance. Whether you’re fresh out of college, starting your first job, or simply looking to improve your financial well-being, this beginner’s guide will equip you with essential tips and strategies to set yourself up for financial success.
From budgeting and saving to investing and debt management, we’ll cover the fundamental principles of personal finance that can help you achieve your financial goals. This article will demystify common financial jargon and provide actionable steps you can take to gain control of your money and build a secure future. Ready to embark on your financial journey? Let’s dive in!
What is Personal Finance?
Personal finance is the management of your money, including budgeting, saving, investing, and protecting your assets. It encompasses all aspects of how you handle your money, from daily expenses to long-term financial goals. In essence, it’s about making informed financial decisions to achieve your financial well-being.
Key Components of Personal Finance:
Personal finance can be broken down into several key components:
- Budgeting: Creating a plan for how you spend your money, ensuring you don’t overspend and can reach your financial goals.
- Saving: Setting aside money for future needs, such as emergencies, retirement, or a down payment on a house.
- Investing: Putting your money to work to grow over time, often through stocks, bonds, or real estate.
- Debt Management: Handling and paying off debt responsibly, minimizing interest costs and avoiding financial distress.
- Insurance: Protecting yourself and your assets from unexpected events, such as accidents, illnesses, or natural disasters.
- Tax Planning: Making strategic financial decisions to minimize your tax liability and maximize your after-tax income.
Why is Personal Finance Important?
Taking control of your personal finances is crucial for several reasons:
- Financial Security: It helps you achieve financial stability and peace of mind, knowing you can manage your finances effectively.
- Goal Achievement: By setting financial goals and making informed decisions, you can reach your aspirations, such as buying a house, traveling the world, or retiring comfortably.
- Avoiding Debt: Managing your finances well reduces the risk of accumulating unnecessary debt and its associated stress.
- Building Wealth: By making smart investment choices and saving diligently, you can grow your wealth over time and secure your future.
Getting Started with Personal Finance:
Here are some basic steps to get started with managing your personal finances:
- Track Your Spending: Monitor where your money is going to identify areas for improvement.
- Create a Budget: Plan how you will spend your income and allocate funds for savings and other financial goals.
- Start Saving: Even small amounts saved regularly can add up over time.
- Manage Your Debt: Prioritize paying down high-interest debt and explore options for debt consolidation.
- Consider Investing: Learn about different investment options and start investing, even if it’s a small amount, to benefit from compounding returns.
Remember, personal finance is a journey, not a destination. It requires ongoing attention and adjustments. By taking proactive steps to manage your money, you can build a strong financial foundation for a more secure and fulfilling future.
The Importance of Budgeting: Tracking Income and Expenses
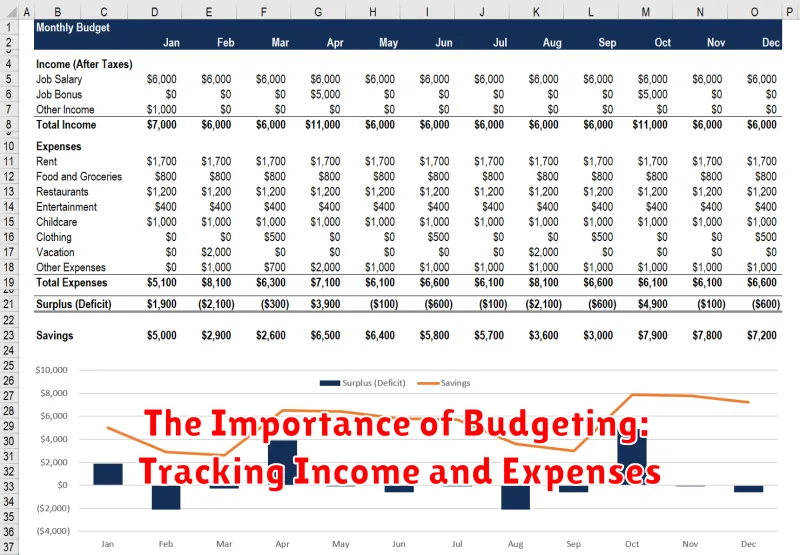
A budget is a financial plan that outlines how you will manage your money. It helps you track your income and expenses, and it can help you achieve your financial goals, such as saving for retirement or buying a house.
There are many benefits to budgeting. It can help you:
- Control your spending and avoid overspending.
- Save money for your goals.
- Reduce stress about your finances.
- Make informed financial decisions.
If you’re not sure where to start with budgeting, there are many resources available to help you. You can find budgeting apps, websites, and books that can guide you through the process.
Here are some tips for creating a budget:
- Track your income and expenses for a few months to get an idea of how much you earn and spend each month.
- Create a budget plan that allocates your income to different categories, such as housing, food, transportation, and entertainment.
- Set realistic goals for your spending and saving.
- Review your budget regularly and make adjustments as needed.
Budgeting can be a powerful tool for achieving your financial goals. By taking the time to create and follow a budget, you can gain control of your finances and set yourself up for financial success.
Creating a Realistic Budget That Works for You
Creating a budget is a crucial step toward achieving your financial goals. It helps you understand your income and expenses, prioritize spending, and save money for the future. However, many people struggle to create a budget that they can stick to. The key to a successful budget is creating a realistic plan that fits your lifestyle and financial situation. This article will guide you through the process of creating a realistic budget that works for you.
1. Track Your Spending
Before you can create a budget, you need to understand where your money is going. For a month, track every dollar you spend, using a spreadsheet, budgeting app, or even a notebook. Be sure to include all expenses, big and small. You can use a budgeting app to categorize your spending, or you can do it manually.
2. Determine Your Income
Once you know your expenses, you need to determine your income. This includes your salary, any other regular income sources, and any potential side income you might earn. Be realistic about your income and don’t rely on potential income that isn’t guaranteed.
3. Create a Spending Plan
Now it’s time to create a spending plan based on your income and expenses. Start by categorizing your expenses into needs and wants. Needs are essential expenses like rent, utilities, groceries, and transportation. Wants are expenses that aren’t necessary for survival, such as entertainment, dining out, and shopping. Once you have your expenses categorized, allocate your income accordingly.
4. Set Realistic Goals
When creating your budget, it’s important to set realistic goals. Don’t try to cut your expenses too drastically or you’re likely to become discouraged and give up. Aim to reduce your spending by a small amount each month, and gradually increase your savings over time. It’s also helpful to have specific financial goals in mind, such as paying off debt, buying a home, or saving for retirement.
5. Use Budgeting Tools
There are many budgeting tools available to help you track your spending and manage your finances. Some popular budgeting apps include Mint, Personal Capital, and YNAB. These apps can automatically categorize your spending, track your progress toward your financial goals, and even help you find ways to save money.
6. Review and Adjust Your Budget
Your budget is a living document that needs to be reviewed and adjusted regularly. As your financial situation changes, your budget will need to change as well. Make sure to review your budget at least once a month and make any necessary adjustments.
7. Be Patient and Persistent
Creating and sticking to a budget takes time and effort. Be patient with yourself and don’t get discouraged if you slip up occasionally. The key is to learn from your mistakes and make adjustments to your budget as needed. With persistence, you can create a realistic budget that works for you and helps you achieve your financial goals.
Identifying and Reducing Unnecessary Spending
In today’s economy, it’s more important than ever to be mindful of your spending. Every dollar counts, and even small changes can make a big difference in your bottom line. Whether you’re trying to save for a specific goal or simply want to have more financial freedom, identifying and reducing unnecessary spending is a crucial step.
Here are some strategies to help you identify and reduce unnecessary spending:
Track Your Spending
The first step to controlling your spending is to understand where your money is going. This can be done by tracking your expenses for a few months, using a spreadsheet, budgeting app, or even simply a notebook. Once you have a clear picture of your spending habits, you can start to identify areas where you can cut back.
Identify “Leaky Buckets”
Once you’ve tracked your spending, look for “leaky buckets”: areas where you’re spending money without realizing it or getting much value in return. This might include things like:
- Subscriptions you don’t use
- Impulse purchases
- Eating out too often
- Unnecessary memberships
Set a Budget
Once you know where your money is going, it’s time to create a budget. This is a plan for how you’ll spend your money each month. A good budget will include:
- Needs: Essentials like housing, food, and transportation.
- Wants: Things you enjoy but don’t absolutely need, like entertainment and dining out.
- Savings: Money you’re setting aside for your goals, like retirement or a down payment on a house.
Use Cash or a Debit Card
Using cash or a debit card can help you stay within your budget. It’s easier to see how much money you have left when you’re physically handing it over or watching the balance in your account decline. Credit cards can lead to overspending and debt, so it’s best to avoid them unless you can pay them off in full each month.
Take Advantage of Deals and Discounts
There are many ways to save money on the things you need and want. Look for coupons, sales, and discounts. Consider shopping at discount stores, buying generic brands, and using comparison websites to find the best deals. You can also save money by taking advantage of free or low-cost activities, such as going for walks, visiting parks, or attending community events.
Make Small Changes
You don’t need to make drastic changes to see a difference in your spending. Even small changes can add up over time. For example, you could:
- Pack your lunch instead of eating out every day.
- Walk or bike instead of driving.
- Shop for groceries at a cheaper store.
- Turn off lights when you leave a room.
Review Your Progress Regularly
It’s important to review your spending and budget regularly to make sure you’re staying on track. This will help you identify areas where you can make adjustments and ensure that you’re making progress towards your financial goals. By reviewing your spending, you can make small but significant adjustments to your lifestyle, maximizing your financial wellbeing and paving the way for a more secure future.
Building an Emergency Fund: Preparing for Unexpected Events

Life is full of surprises, and not all of them are pleasant. Unexpected expenses can pop up at any time, from a sudden car repair to a medical emergency. That’s why building an emergency fund is crucial. It’s your financial safety net, providing a cushion to absorb financial shocks and keep you from spiraling into debt.
Why is an emergency fund so important?
An emergency fund acts as a financial buffer, shielding you from the stress and hardship of unexpected events. Here’s why it’s essential:
- Avoids debt: By having readily available cash, you can avoid taking on high-interest loans or credit card debt to cover unexpected expenses.
- Provides peace of mind: Knowing you have financial reserves to fall back on reduces anxiety and stress, allowing you to focus on addressing the situation rather than worrying about finances.
- Enables better financial decisions: A strong emergency fund gives you the freedom to make responsible financial choices, such as waiting for a better deal on a car or taking advantage of a job opportunity that may involve a temporary relocation.
- Protects your savings: In times of emergency, you won’t have to dip into your long-term savings goals, like retirement funds or college savings, ensuring your financial plans stay on track.
How much should you save?
The ideal amount for your emergency fund depends on your individual circumstances, but most experts recommend having 3 to 6 months’ worth of essential living expenses saved. This includes rent or mortgage payments, utilities, groceries, transportation, and other necessary costs.
Tips for building your emergency fund:
- Set a realistic goal: Start small and gradually increase your savings. Even saving $50 or $100 per month can make a difference over time.
- Automate your savings: Set up automatic transfers from your checking account to your savings account. This makes saving consistent and effortless.
- Find extra income: Look for ways to earn additional income, such as a side hustle, freelance work, or selling unused items.
- Track your spending: Monitor your expenses to identify areas where you can cut back and redirect those funds to your emergency savings.
- Be patient and persistent: Building an emergency fund takes time, so stay committed and don’t get discouraged by slow progress. Every little bit counts.
In conclusion, building an emergency fund is an essential part of responsible financial planning. It provides a safety net for unexpected events, reduces stress, and empowers you to make sound financial decisions. By following these tips, you can create a financial cushion that will help you weather any storm life throws your way.
Managing Debt: Paying Down Credit Cards and Loans
Debt can be a heavy burden, weighing down your finances and causing stress. Whether it’s from credit cards, student loans, or personal loans, managing debt effectively is crucial for achieving financial freedom and peace of mind.
Understanding Your Debt
The first step is to understand the nature and extent of your debt. Make a list of all your outstanding debts, including:
- Credit card balances
- Loan amounts (student, personal, car, etc.)
- Interest rates and minimum payments
This information will help you create a plan for paying down your debt.
Debt Reduction Strategies
Several strategies can help you tackle debt effectively:
- Snowball Method: This method involves focusing on paying off the debt with the smallest balance first, while making minimum payments on the others. The feeling of accomplishment from paying off a debt quickly can motivate you to keep going.
- Avalanche Method: This method focuses on paying off the debt with the highest interest rate first, regardless of the balance. While it may take longer to see initial results, it can save you money in the long run by minimizing interest charges.
- Debt Consolidation: This involves combining multiple debts into a single loan with a lower interest rate. While this can reduce your monthly payments, it’s important to ensure you have a clear repayment plan to avoid further accumulation of debt.
Tips for Debt Management
Here are some tips for managing your debt effectively:
- Create a Budget: Track your income and expenses to understand where your money is going. A budget can help you identify areas where you can cut back to free up funds for debt repayment.
- Negotiate with Creditors: Don’t be afraid to negotiate with your creditors. They may be willing to lower your interest rates or offer a payment plan to help you get back on track.
- Avoid New Debt: Once you’ve started paying down debt, resist the urge to accumulate new debt. Focus on sticking to your budget and building a strong financial foundation.
- Seek Professional Help: If you’re struggling to manage debt on your own, consider seeking advice from a financial advisor or credit counselor. They can provide personalized guidance and support.
Conclusion
Managing debt effectively requires discipline, planning, and a commitment to financial responsibility. By understanding your debt, implementing a strategic plan, and following these tips, you can make significant progress towards becoming debt-free. Remember, achieving financial freedom is a journey, and with patience and perseverance, you can overcome any debt-related challenges and achieve your financial goals.
Saving for the Future: Short-Term and Long-Term Goals
Saving money is essential for a secure financial future. It allows you to achieve your financial goals, both in the short term and the long term. Whether you’re saving for a new car, a down payment on a house, or retirement, having a well-defined savings plan is crucial. This article will delve into the importance of setting short-term and long-term goals and how to create a savings strategy that aligns with your aspirations.
Short-Term Goals
Short-term goals are typically financial targets that you aim to achieve within a year or less. These goals are often more tangible and easier to visualize, which can make them motivating. Some common examples of short-term goals include:
- Saving for a vacation
- Paying off debt
- Making a large purchase like a new appliance
- Building an emergency fund
To achieve short-term goals, it’s essential to set a specific savings amount, determine a realistic timeline, and establish a consistent savings strategy. You can use tools like budgeting apps or spreadsheets to track your progress and ensure you’re on track.
Long-Term Goals
Long-term goals are financial objectives that you plan to achieve over a longer period, often several years or even decades. These goals typically require more significant planning and consistent saving habits. Examples of long-term goals include:
- Saving for retirement
- Paying for a child’s education
- Investing in real estate
- Starting a business
Long-term goals often involve more complex financial strategies, such as investing in stocks, bonds, or real estate. It’s crucial to seek advice from a financial advisor to develop a comprehensive plan that aligns with your risk tolerance and investment objectives.
Balancing Short-Term and Long-Term Goals
Balancing short-term and long-term goals is key to achieving financial success. You don’t have to choose between them. Instead, you can create a balanced savings plan that addresses both your immediate needs and your future aspirations. One approach is to allocate a portion of your savings towards short-term goals while consistently contributing to long-term investments.
Tips for Saving for the Future
Here are some practical tips to help you save for the future:
- Create a Budget: Track your income and expenses to identify areas where you can cut back.
- Automate Your Savings: Set up automatic transfers to your savings account from your checking account.
- Increase Your Income: Consider ways to earn more money, such as taking on a side hustle or negotiating a raise.
- Invest Wisely: Explore different investment options, such as stocks, bonds, or mutual funds, based on your risk tolerance and financial goals.
- Review Your Savings Regularly: Ensure your savings plan is still aligned with your changing needs and goals.
Saving for the future requires discipline, planning, and a long-term perspective. By setting clear short-term and long-term goals and implementing a consistent savings strategy, you can build a secure financial future for yourself and your loved ones.
Understanding Credit Scores and Credit Reports
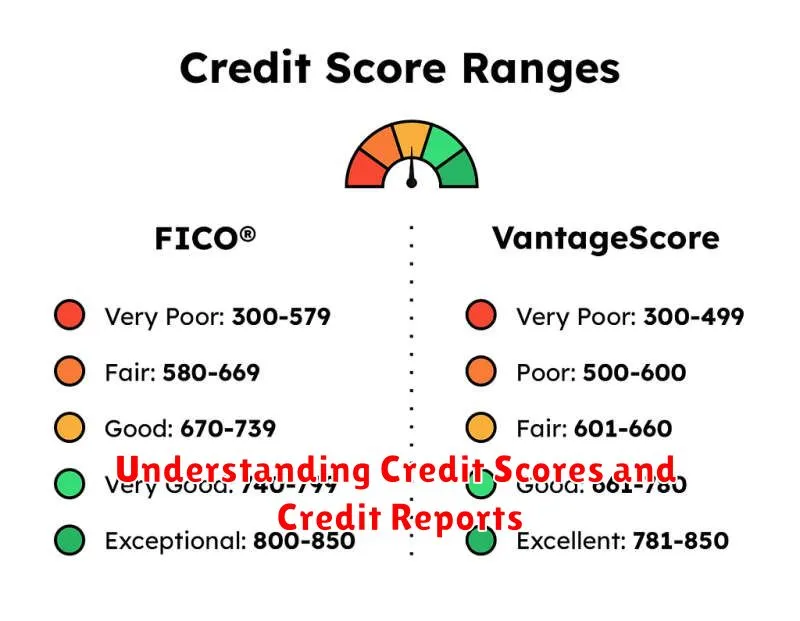
Your credit score is a numerical representation of your creditworthiness, based on your credit history. It’s a critical factor that lenders use to assess your risk and determine if they should grant you a loan, the interest rate they’ll charge, and the credit limit they’ll offer.
Your credit report is a detailed document that outlines your credit history. It includes information like your payment history, outstanding balances, credit utilization, and any negative marks such as late payments or defaults.
There are three major credit reporting agencies in the US: Experian, Equifax, and TransUnion. Each agency maintains its own credit report on you, and these reports may not always be identical due to slight variations in the data they collect and the way they process it.
Understanding your credit score and report is crucial for several reasons:
- Securing loans: A good credit score increases your chances of getting approved for loans and credit cards, and securing favorable terms.
- Lower interest rates: A higher score typically translates to lower interest rates, saving you money in the long run.
- Better rental prospects: Some landlords use credit scores to assess the financial reliability of potential tenants.
- Job opportunities: Some employers may check your credit score as part of their background check process, especially for positions that involve handling sensitive financial information.
To access your credit report, you can request a free copy annually from each of the three credit bureaus through AnnualCreditReport.com. You can also purchase your credit score from credit bureaus or credit monitoring services.
It’s important to regularly review your credit reports for any errors or inaccuracies. You have the right to dispute any incorrect information and request a correction. By understanding your credit score and report, you can take proactive steps to improve your financial standing and achieve your financial goals.
Protecting Yourself from Financial Fraud
Financial fraud is a serious problem that can affect anyone. It can take many forms, from identity theft to investment scams. Financial fraud can have a devastating impact on your finances and your life. That’s why it’s important to take steps to protect yourself.
Here are some tips on how to protect yourself from financial fraud:
Be aware of the different types of financial fraud. There are many different types of financial fraud, so it’s important to be aware of them all. Some common types of fraud include:
- Identity theft
- Credit card fraud
- Phishing scams
- Investment scams
Protect your personal information. This includes your Social Security number, credit card numbers, and bank account information. Don’t share this information with anyone you don’t know and trust.
Be wary of unsolicited offers. If you receive an offer that seems too good to be true, it probably is. Don’t give out any personal information to someone who has contacted you out of the blue.
Monitor your accounts regularly. Check your credit card statements, bank statements, and other financial accounts for any suspicious activity. If you see anything that doesn’t look right, report it to your financial institution immediately.
Be careful about what you post online. Don’t post your personal information on social media or other public websites. Be aware that scammers can use this information to target you.
If you think you’ve been a victim of financial fraud, report it to the authorities. You can report financial fraud to the Federal Trade Commission (FTC), the U.S. Postal Inspection Service, or your local police department.
Seeking Financial Education and Resources
In today’s complex financial world, it’s more crucial than ever to be financially literate and equipped with the right resources to make informed decisions about your money. Whether you’re just starting out, managing debt, planning for retirement, or anything in between, seeking financial education and resources can empower you to achieve your financial goals.
Understanding your finances is the foundation of financial well-being. This includes knowing your income, expenses, assets, and debts. Once you have a clear picture of your current financial situation, you can start making informed decisions about budgeting, saving, and investing.
Financial literacy resources are readily available and can be tailored to your specific needs. Here are some valuable resources to consider:
- Online Courses and Programs: Platforms like Coursera, edX, and Khan Academy offer free or affordable courses on personal finance, investing, budgeting, and more.
- Financial Institutions: Your bank or credit union may provide free financial education workshops, seminars, or online resources.
- Government Agencies: Websites like the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB) and the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) offer valuable information and tools for consumers.
- Non-profit Organizations: Organizations like the National Endowment for Financial Education (NEFE) and the Jump$tart Coalition for Personal Financial Literacy provide financial education programs and resources.
- Financial Advisors: If you’re seeking personalized financial advice, consider consulting with a qualified financial advisor.
Investing in your financial education is an investment in your future. By taking the time to learn about personal finance, you can gain the knowledge and skills to make sound financial decisions that will help you reach your goals and achieve financial security.

