Are you a high-income earner looking for ways to grow and protect your wealth? If so, you’re not alone. Many successful individuals are faced with the challenge of managing their finances effectively. While earning a high income is certainly a good starting point, it’s not enough to guarantee long-term financial security. Strategic wealth management is essential to ensure your hard-earned money works for you, not against you.
This guide will delve into a variety of wealth management strategies specifically tailored for high-income earners. We will explore crucial topics such as investment diversification, tax optimization, estate planning, and risk management. By understanding and implementing these strategies, you can gain greater control over your financial future and achieve your wealth goals.
Tax Optimization Strategies for High Earners
High earners face unique tax challenges. With higher incomes, they are subject to higher tax brackets and may be subject to various state and federal taxes. Fortunately, there are several tax optimization strategies that can help high earners reduce their tax liability and maximize their after-tax income.
1. Tax Planning
Proactive tax planning is crucial. This involves understanding your current tax situation and anticipating future changes. A tax professional can help you develop a comprehensive tax plan that minimizes your tax burden throughout the year. This might include:
- Optimizing deductions and credits: Identifying and maximizing eligible deductions and credits can significantly reduce your taxable income.
- Tax-loss harvesting: Selling losing investments to offset capital gains and reduce your overall tax liability.
- Estate planning: Strategically planning for the transfer of wealth can minimize estate taxes and ensure your assets are distributed as intended.
2. Retirement Savings
Maximizing contributions to retirement accounts is a powerful way to reduce your taxable income and save for the future. These accounts offer tax advantages, such as tax-deferred growth or tax-free withdrawals.
- 401(k) and 403(b): Employer-sponsored retirement plans that allow pre-tax contributions.
- IRA (Individual Retirement Account): Traditional and Roth IRAs offer different tax benefits based on your needs.
3. Charitable Giving
Donating to charity can provide tax benefits and support worthy causes. Charitable contributions are often deductible, reducing your taxable income.
- Cash donations: Deduct up to 60% of your Adjusted Gross Income (AGI) for cash donations.
- Donating appreciated assets: Gifting appreciated assets, such as stocks or real estate, allows you to avoid capital gains tax and receive a deduction for the fair market value.
4. Investment Strategies
Strategic investments can provide tax benefits and long-term growth. Consider:
- Tax-advantaged investments: Investments within accounts like 401(k)s or IRAs benefit from tax-deferred growth.
- Municipal bonds: Interest earned on municipal bonds is often tax-free at the federal level and potentially at the state level.
- Tax-loss harvesting: Selling losing investments to offset capital gains and reduce your overall tax liability.
5. Seeking Professional Advice
It’s essential to seek advice from a qualified tax professional. They can help you navigate the complexities of tax laws, identify all eligible deductions and credits, and develop a tailored tax optimization strategy that meets your specific financial situation.
By implementing these tax optimization strategies, high earners can minimize their tax liability and maximize their after-tax income. Remember, tax laws are complex and can change frequently, so staying informed and seeking professional advice is crucial.
Estate Planning and Wealth Preservation
Estate planning is the process of preparing for the transfer of your assets after death. It is an essential part of financial planning and can help you protect your loved ones and ensure that your wealth is distributed according to your wishes.
Wealth preservation, on the other hand, refers to strategies that are designed to protect and grow your assets over time. This can include investments, insurance, and tax planning. Both estate planning and wealth preservation are important for individuals who want to secure their financial future and provide for their loved ones.
Key Components of Estate Planning
A comprehensive estate plan typically includes the following components:
- Will: A legal document that outlines how your assets will be distributed after your death.
- Trust: A legal entity that can hold and manage your assets for the benefit of your beneficiaries.
- Power of Attorney: A document that authorizes someone to make financial and legal decisions on your behalf if you become incapacitated.
- Living Will: A document that expresses your wishes regarding end-of-life care.
Benefits of Estate Planning
There are many benefits to creating an estate plan, including:
- Ensure your assets are distributed according to your wishes.
- Minimize estate taxes.
- Protect your loved ones from financial hardship.
- Avoid legal disputes after your death.
- Provide for the care of minor children or disabled adults.
Wealth Preservation Strategies
Wealth preservation strategies can help you protect and grow your assets over time. Some common strategies include:
- Diversification: Spreading your investments across different asset classes to reduce risk.
- Insurance: Protecting your assets from unexpected events, such as illness, disability, or death.
- Tax planning: Minimizing your tax liability through strategies such as tax-advantaged accounts and charitable giving.
Conclusion
Estate planning and wealth preservation are essential components of financial planning. By taking the time to create a comprehensive plan, you can ensure that your assets are protected, your wishes are carried out, and your loved ones are taken care of.
Investment Strategies for High-Net-Worth Individuals
High-net-worth individuals (HNWIs) face unique challenges when it comes to investing. They have a greater need for sophisticated strategies to manage their wealth, protect their assets, and achieve their financial goals. This article will explore some of the key investment strategies that are commonly used by HNWIs.
Diversification
Diversification is a fundamental principle of investing that involves spreading your investments across different asset classes, such as stocks, bonds, real estate, and commodities. This helps to reduce risk by ensuring that your portfolio is not overly exposed to any single asset class. For HNWIs, diversification can take on a more sophisticated form, with investments in alternative assets such as private equity, hedge funds, and venture capital.
Tax Optimization
Tax optimization is another crucial aspect of investing for HNWIs. As their income and assets grow, they face a higher tax burden. Strategies for tax optimization can include using tax-advantaged accounts such as IRAs and 401(k)s, taking advantage of tax deductions and credits, and structuring investments in a way that minimizes tax liability.
Estate Planning
Estate planning is essential for HNWIs to ensure that their assets are distributed according to their wishes and to minimize the tax burden on their heirs. This may involve creating trusts, setting up charitable foundations, and implementing other strategies to transfer wealth effectively.
Active Management
Many HNWIs choose to work with professional financial advisors to actively manage their investments. These advisors have the expertise and resources to develop customized investment strategies and to monitor market trends and make adjustments as needed. Active management can be particularly valuable for investors with complex financial situations or specific goals.
Alternative Investments
Alternative investments, such as private equity, hedge funds, and real estate, offer the potential for higher returns but also carry greater risk. HNWIs may allocate a portion of their portfolio to these investments to diversify and potentially enhance returns. However, it is important to carefully evaluate the risks and potential rewards before investing in alternative assets.
Conclusion
Investing for HNWIs is a multifaceted process that requires careful planning and execution. By employing strategies such as diversification, tax optimization, estate planning, active management, and alternative investments, HNWIs can effectively manage their wealth and achieve their financial goals. It is important to work with a qualified financial advisor to develop a tailored investment plan that meets their unique needs and objectives.
Philanthropic Giving and Impact Investing
Philanthropic giving and impact investing are two distinct but related approaches to using wealth for good. Both focus on making a positive impact on the world, but they differ in their goals, methods, and expected returns.
Philanthropic Giving
Philanthropic giving is the act of donating money, time, or resources to charitable causes. It is typically driven by altruistic motivations, such as a desire to alleviate suffering, promote social justice, or support education and the arts.
Key features of philanthropic giving include:
- Non-profit focus: Philanthropic donations are typically made to non-profit organizations or charities.
- No expectation of return: Philanthropic giving is not expected to generate a financial return. The primary goal is to make a positive social impact.
- Variety of forms: Philanthropic giving can take many forms, including cash donations, in-kind contributions, and volunteer work.
Impact Investing
Impact investing is a form of investing that seeks to generate both financial returns and positive social or environmental impact. It involves investing in companies, organizations, or projects that are explicitly designed to address social and environmental challenges.
Key features of impact investing include:
- Double bottom line: Impact investors aim to achieve both financial returns and social impact.
- Measurable impact: Impact investors seek to measure and track the social and environmental impact of their investments.
- Range of investment strategies: Impact investing encompasses a wide range of investment strategies, from venture capital and private equity to debt financing and public markets.
Similarities and Differences
Both philanthropic giving and impact investing share the common goal of making a positive impact on the world. However, they differ in their approach and expected outcomes:
| Feature | Philanthropic Giving | Impact Investing |
|---|---|---|
| Goal | Social impact | Financial return and social impact |
| Returns | No expectation of financial return | Expectation of financial return |
| Investment Vehicles | Non-profit organizations, charities | Companies, organizations, or projects with social or environmental impact |
| Measurement | Qualitative impact assessment | Quantitative impact measurement |
Conclusion
Philanthropic giving and impact investing offer distinct but complementary ways to utilize wealth for good. Philanthropic giving provides a powerful tool for addressing immediate social needs, while impact investing offers a potential for both financial returns and long-term sustainable impact. By understanding the nuances of each approach, individuals and institutions can make informed decisions about how to allocate their resources to achieve their desired social and financial goals.
Managing Concentrated Stock Positions

A concentrated stock position occurs when a significant portion of an investor’s portfolio is allocated to a single stock or a small number of stocks. This can be a lucrative strategy, but it also comes with significant risks. If the investment performs well, investors can experience outsized returns. However, if the investment performs poorly, the impact on the overall portfolio can be substantial.
There are several reasons why investors might find themselves with concentrated stock positions. Some common reasons include:
- Employee Stock Options (ESOs): Many companies offer ESOs to their employees, which can lead to a concentration of stock in the company.
- Inheritance: Inherited assets often include a significant portion of a single stock or a few stocks.
- Strong Belief in a Company: Investors may have a strong conviction in a particular company’s future prospects and allocate a large portion of their portfolio to its stock.
While concentrated stock positions can be beneficial, it’s crucial to manage the risks associated with them. Here are some strategies for managing concentrated stock positions:
Diversification
Diversification is key to mitigating risk. Investors with concentrated positions can diversify by adding other assets to their portfolio, such as bonds, real estate, or other stocks. This helps to reduce the impact of any single stock’s performance on the overall portfolio.
Tax-Loss Harvesting
Tax-loss harvesting involves selling losing investments to offset capital gains and reduce your tax liability. This strategy can be particularly useful for concentrated stock positions, as it allows investors to reduce the overall impact of losses.
Selling Covered Calls
Selling covered calls involves selling call options on a stock that you own. This strategy generates income and can help to offset potential losses. However, it also limits potential upside gains.
Collar Strategy
A collar strategy involves buying a put option and selling a call option on the same underlying stock. This strategy protects the downside while limiting potential upside gains. It can be a useful strategy for investors who want to reduce risk without completely divesting from the stock.
Managing concentrated stock positions requires careful planning and execution. It’s essential to consider the risks and potential benefits before making any decisions. Consulting with a financial advisor can provide valuable insights and guidance.
Building a Diversified Investment Portfolio
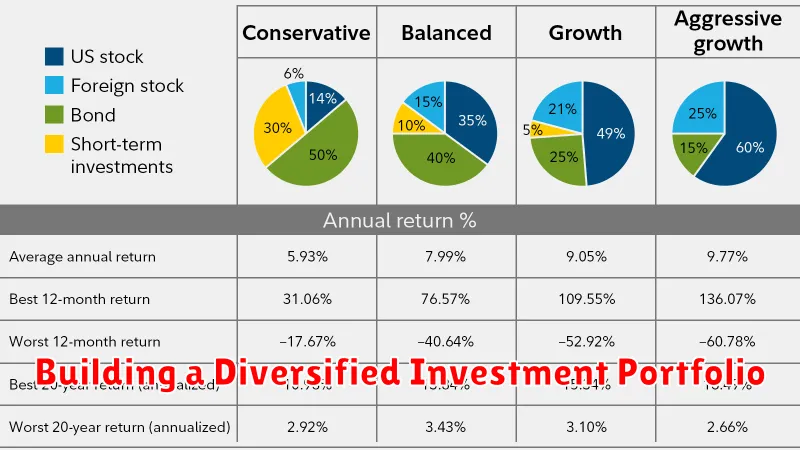
A diversified investment portfolio is crucial for mitigating risk and maximizing returns over the long term. By spreading your investments across different asset classes, you can reduce the impact of any single investment’s performance on your overall portfolio. This article will guide you through the process of building a diversified investment portfolio, considering factors like risk tolerance, investment goals, and time horizon.
Understanding Asset Classes
Asset classes represent different types of investments with varying risk and return profiles. Some common asset classes include:
- Stocks: Represent ownership in publicly traded companies. They generally offer higher potential returns but also carry greater risk.
- Bonds: Represent loans to companies or governments, offering lower potential returns but also lower risk compared to stocks.
- Real Estate: Includes physical property like homes, apartments, and commercial buildings. It can offer diversification and potential for appreciation, but also involves higher transaction costs and illiquidity.
- Commodities: Represent raw materials like gold, oil, and agricultural products. They can act as a hedge against inflation and provide diversification but also carry higher volatility.
- Cash: Represents liquid assets like savings accounts and money market funds. While offering low returns, it provides stability and liquidity.
Determining Your Risk Tolerance
Before investing, it’s essential to understand your risk tolerance, which reflects your willingness to accept potential losses in exchange for potentially higher returns. Factors to consider include:
- Time horizon: Longer investment horizons generally allow for greater risk-taking, as there’s more time to recover from potential losses.
- Financial situation: Your current income, savings, and debt obligations influence how much risk you can afford to take.
- Personal goals: Your investment goals, whether it’s retirement planning, education savings, or buying a home, will determine the appropriate risk level.
Setting Investment Goals
Having clear investment goals provides direction and helps you choose appropriate investments. Examples of investment goals include:
- Retirement planning: Accumulating enough wealth to support your lifestyle during retirement.
- Education savings: Saving for your children’s or grandchildren’s college education.
- Down payment for a home: Saving for a down payment on a house or other property.
Choosing Investments
Once you’ve determined your risk tolerance and investment goals, you can choose specific investments within each asset class. Consider factors like:
- Fees and expenses: Look for investments with low fees, as these can significantly impact returns over time.
- Investment strategy: Active or passive investing approaches have different advantages and drawbacks.
- Liquidity: Ensure that your investments are readily convertible to cash when needed.
Rebalancing Your Portfolio
Over time, the asset allocation of your portfolio may drift due to market fluctuations. It’s crucial to rebalance your portfolio periodically to maintain your desired asset allocation. This involves selling investments that have performed well and buying those that have underperformed to bring your portfolio back in line with your original strategy.
Conclusion
Building a diversified investment portfolio is an ongoing process that requires careful planning, monitoring, and adjustments. By understanding asset classes, your risk tolerance, investment goals, and choosing appropriate investments, you can create a portfolio that aligns with your financial objectives and helps you achieve your long-term financial goals.
Seeking Expert Financial and Legal Advice

Navigating the complexities of finance and law can be overwhelming, even for seasoned individuals. Whether you’re facing a significant financial decision, legal dispute, or simply seeking guidance, consulting with an expert can make all the difference.
Financial Advice
Financial advisors provide personalized guidance on managing your finances, investments, and retirement planning. They can help you:
- Develop a financial plan tailored to your goals and risk tolerance.
- Manage investments and optimize portfolio performance.
- Plan for retirement and ensure financial security in your later years.
Legal Advice
Legal professionals offer expertise in a wide range of legal matters, from contract review and estate planning to litigation and criminal defense. Engaging a lawyer can:
- Protect your rights and interests.
- Provide legal guidance and representation in legal proceedings.
- Help you navigate complex legal situations.
Finding the Right Expert
When choosing a financial advisor or lawyer, it’s crucial to do your research and find someone with the necessary experience and qualifications. Consider factors such as:
- Expertise and Specialization: Ensure the advisor or lawyer specializes in the area you need assistance with.
- Credentials and Licenses: Verify their qualifications and licensing.
- Reputation and Client Testimonials: Seek recommendations and read reviews from previous clients.
- Communication and Trust: Find someone you feel comfortable communicating with and trust to represent your best interests.
The Value of Professional Advice
Seeking professional advice from a reputable financial advisor or lawyer can offer significant benefits, including:
- Peace of Mind: Knowing you have expert guidance can alleviate stress and anxiety.
- Informed Decision-Making: You’ll have access to accurate information and tailored solutions.
- Increased Financial Security: Proper financial planning and legal protection can safeguard your assets and future.
Don’t hesitate to seek professional advice when navigating complex financial or legal matters. It can make a significant difference in achieving your goals and protecting your interests.
Planning for Retirement and Legacy Goals
Retirement is a significant life milestone that requires meticulous planning and consideration. While securing financial stability is crucial, it’s equally important to contemplate your legacy and the impact you want to leave on the world.
Planning for retirement involves setting financial goals, determining your desired lifestyle, and creating a comprehensive strategy to achieve them. It’s essential to consider factors such as your current savings, income, expenses, and expected longevity.
Financial Goals:
Setting clear financial goals is paramount for a successful retirement plan. These goals could include:
- Accumulating a specific retirement nest egg.
- Maintaining your current lifestyle.
- Traveling and pursuing hobbies.
- Providing for your loved ones.
Legacy Goals:
Your legacy goals are aspirations you want to achieve beyond your lifetime. These goals could involve:
- Leaving an inheritance to your family.
- Supporting charitable causes.
- Creating a lasting impact on your community.
- Preserving your family history.
Integrating Retirement and Legacy Planning:
Integrating retirement and legacy planning allows you to maximize your impact and ensure your financial well-being while leaving a lasting legacy. This involves:
- Establishing a trust or estate plan to distribute assets.
- Identifying beneficiaries and their needs.
- Considering tax implications and estate planning strategies.
- Setting aside funds for charitable donations.
Professional Guidance:
Seeking professional guidance from a financial advisor and estate planning attorney can help you navigate the complexities of retirement and legacy planning. These professionals can provide personalized advice, ensure your goals are aligned with your financial situation, and guide you through the legal and tax considerations involved.
Retirement and legacy planning are interconnected processes that require careful attention to detail. By establishing clear goals, creating a comprehensive plan, and seeking professional support, you can secure your future and leave a meaningful legacy for generations to come.

