Looking to build long-term wealth but feel intimidated by the stock market? You’re not alone. Many people are hesitant to invest because they don’t know where to start. But here’s a secret: you don’t need to be a Wall Street expert to grow your money. Index funds are one of the simplest and most effective ways to invest for the future.
These low-cost funds track the performance of a specific market index, such as the S&P 500. This means you’re essentially investing in a basket of hundreds of companies, diversifying your portfolio and reducing risk. By investing in index funds, you can gain exposure to the overall market’s growth without needing to pick individual stocks. This makes them a great choice for long-term investing, especially for beginners.
What are Index Funds and How Do They Work?
Index funds are a type of mutual fund or exchange-traded fund (ETF) that tracks the performance of a specific market index, such as the S&P 500 or the Nasdaq 100. They aim to replicate the performance of the index by holding the same securities in the same proportions as the index.
Key Features of Index Funds:
Index funds offer several key features that make them attractive to investors:
- Diversification: Index funds provide instant diversification by investing in a wide range of companies within a specific market.
- Low Costs: Index funds typically have lower expense ratios than actively managed funds, as they require less research and management.
- Passive Management: Index funds are passively managed, meaning they don’t try to beat the market. They simply track the performance of their underlying index.
- Transparency: The holdings and performance of index funds are transparent, as they are publicly tracked by their respective indices.
How Index Funds Work:
Index funds work by holding a basket of securities that mirror the composition of their target index. When the index goes up or down, the value of the index fund’s shares will also go up or down in a similar proportion. For example, if the S&P 500 index rises by 2%, an S&P 500 index fund will likely also rise by approximately 2%.
Benefits of Investing in Index Funds:
Investing in index funds offers several benefits, including:
- Potential for Long-Term Growth: Index funds have historically provided strong returns over long periods.
- Simplicity and Ease of Use: Index funds are relatively easy to understand and invest in.
- Lower Risk Compared to Individual Stocks: By investing in a diversified basket of securities, index funds reduce the risk associated with individual stocks.
Types of Index Funds:
There are various types of index funds available, including:
- Broad Market Index Funds: Track the performance of the entire stock market, such as the S&P 500 or the Dow Jones Industrial Average.
- Sector Index Funds: Focus on a specific industry or sector, such as technology or healthcare.
- International Index Funds: Invest in securities from markets outside the United States.
- Bond Index Funds: Track the performance of various bond indices, such as the Barclays Aggregate Bond Index.
Conclusion:
Index funds offer a simple, cost-effective, and diversified way to invest in the stock market. They are suitable for both new and experienced investors seeking long-term growth potential with lower risk compared to individual stocks. By understanding the basics of index funds, investors can make informed decisions about their investment strategies.
Benefits of Index Fund Investing

Index funds are a type of mutual fund or exchange-traded fund (ETF) that tracks a specific market index, such as the S&P 500 or the Nasdaq 100. They aim to replicate the performance of the index as closely as possible by investing in the same securities in the same proportions as the index.
Index fund investing has become increasingly popular in recent years due to several key benefits:
1. Low Costs
Index funds typically have lower expense ratios than actively managed funds. This is because they do not require the same level of research, analysis, and trading activity. Lower expense ratios mean that more of your investment returns are retained for you.
2. Diversification
By tracking a broad market index, index funds provide instant diversification across a wide range of securities. This helps to mitigate risk by reducing your exposure to any single company or sector.
3. Simplicity
Index funds are relatively simple to understand and invest in. They do not require you to make complex investment decisions or keep up with market news constantly.
4. Long-Term Growth
Over the long term, index funds have consistently outperformed actively managed funds. This is because they are designed to track the overall market, which tends to grow over time.
5. Tax Efficiency
Index funds are generally more tax-efficient than actively managed funds. This is because they trade less frequently, resulting in fewer taxable events.
If you’re looking for a low-cost, diversified, and simple way to invest for the long term, index funds are an excellent choice.
Choosing the Right Index Funds for Your Portfolio
Index funds are a popular investment option for many investors, as they offer a low-cost way to gain exposure to a broad range of assets. However, with so many different index funds available, choosing the right ones for your portfolio can be a challenge. This article will provide a guide to help you select the index funds that best meet your investment goals.
Understanding Index Funds
Index funds are passively managed mutual funds or exchange-traded funds (ETFs) that track a specific market index, such as the S&P 500 or the Nasdaq 100. The fund’s portfolio mirrors the composition of the index, buying and selling securities in the same proportions as the index. This means that the fund’s performance will closely track the performance of the underlying index.
Benefits of Index Funds
Index funds offer a number of advantages for investors:
- Low Costs: Index funds typically have lower expense ratios than actively managed funds, as they don’t require the same level of research and trading.
- Diversification: Index funds provide instant diversification across a wide range of securities, reducing risk.
- Transparency: The holdings of an index fund are clearly defined by the underlying index, making it easy to see what you’re investing in.
- Tax Efficiency: Index funds tend to have lower turnover rates, resulting in fewer taxable events.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Index Funds
When choosing index funds, it’s important to consider the following factors:
- Investment Goals: What are you trying to achieve with your investment? Are you saving for retirement, buying a house, or simply growing your wealth?
- Risk Tolerance: How much risk are you willing to take on? Index funds can range in risk, from low-risk bond funds to high-risk stock funds.
- Time Horizon: How long do you plan to hold your investment? Index funds are generally best suited for long-term investments.
- Expense Ratio: The expense ratio is the annual fee charged by the fund manager. Look for funds with low expense ratios.
- Tracking Error: This measures how closely the fund’s performance tracks the underlying index. Aim for funds with low tracking errors.
Types of Index Funds
There are many different types of index funds, each tracking a different market index. Some of the most popular include:
- S&P 500 Funds: These funds track the S&P 500 index, which represents the 500 largest publicly traded companies in the United States.
- Nasdaq 100 Funds: These funds track the Nasdaq 100 index, which represents the 100 largest non-financial companies listed on the Nasdaq Stock Market.
- Total Stock Market Funds: These funds track a broad range of U.S. stocks, providing exposure to both large-cap and small-cap companies.
- International Stock Funds: These funds invest in stocks outside of the United States, diversifying your portfolio across global markets.
- Bond Funds: These funds invest in bonds, offering a lower-risk alternative to stocks.
Conclusion
Choosing the right index funds for your portfolio is an important decision. By understanding your investment goals, risk tolerance, and time horizon, and by considering factors like expense ratios and tracking errors, you can select index funds that are appropriate for your needs and help you achieve your financial goals.
Understanding Expense Ratios and Fees
When investing, it’s crucial to understand the costs involved, including expense ratios and fees. These charges can significantly impact your overall returns. This article aims to provide a clear explanation of expense ratios and fees, helping you make informed investment decisions.
Expense Ratios
An expense ratio is a percentage of your investment’s assets that is charged annually to cover the fund’s operating expenses. These expenses can include management fees, administrative costs, marketing expenses, and trading commissions.
For example, a mutual fund with an expense ratio of 1% will deduct 1% of your investment value each year to cover its expenses. This means that if you invest $10,000, the fund will charge $100 in annual expenses.
Types of Fees
In addition to expense ratios, there are various other fees associated with investing. Some common fees include:
- Load Fees: These are one-time charges that are paid when you buy or sell shares in a mutual fund. They are typically expressed as a percentage of the investment amount.
- Front-end load: Paid when you buy shares.
- Back-end load: Paid when you sell shares.
- Trading Commissions: These are fees charged for buying or selling securities.
- Account Maintenance Fees: Some investment accounts may charge a monthly or annual fee for maintenance.
- Advisory Fees: These are fees charged by financial advisors for providing investment advice.
Impact of Fees
Even seemingly small fees can have a significant impact on your investment returns over time. This is due to the power of compounding, where your earnings earn interest or returns, further increasing your wealth. Higher fees reduce your overall returns, meaning you will have less money at the end of the investment period.
How to Find Expense Ratios and Fees
You can typically find information about expense ratios and fees in the fund’s prospectus or fact sheet. It’s also essential to read the disclosures provided by your broker or investment platform.
Tips for Minimizing Fees
Here are some tips to minimize fees and maximize your investment returns:
- Choose index funds or ETFs with low expense ratios.
- Avoid funds with high loads or other unnecessary fees.
- Shop around for brokers or investment platforms with low account maintenance fees.
- Consider using a robo-advisor for automated, low-cost investment management.
Conclusion
Understanding expense ratios and fees is critical for making informed investment decisions. By carefully considering these costs and seeking out options with low fees, you can maximize your returns over the long term.
Opening a Brokerage Account
Opening a brokerage account is the first step to investing in the stock market. It allows you to buy and sell securities, such as stocks, bonds, and mutual funds. While it may seem daunting, the process is actually quite simple. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you get started:
1. Choose a Brokerage
The first step is to choose a brokerage firm. There are many different brokerages available, each with its own set of fees, features, and investment options. Consider factors such as:
- Fees: Brokerages charge fees for various services, such as trading commissions, account maintenance, and inactivity fees. Compare the fee structures of different brokerages to find one that fits your budget.
- Investment Options: Make sure the brokerage offers the types of investments you want to buy, such as stocks, bonds, ETFs, or mutual funds.
- Research Tools: Some brokerages provide extensive research tools, such as real-time quotes, charting software, and analyst reports. These can be helpful for making informed investment decisions.
- Customer Service: Choose a brokerage with responsive and helpful customer service, especially if you’re a beginner investor.
2. Open an Account
Once you’ve chosen a brokerage, you’ll need to open an account. This typically involves providing personal information, such as your name, address, and Social Security number. You’ll also need to choose an account type, such as a cash account, margin account, or retirement account. Some brokerages may require a minimum deposit to open an account.
3. Fund Your Account
After your account is opened, you’ll need to fund it with money to start investing. You can deposit funds through a variety of methods, including bank transfers, wire transfers, or checks. The time it takes for funds to be deposited into your account varies depending on the method used.
4. Start Trading
Once your account is funded, you’re ready to start trading. You can buy and sell securities through the brokerage’s online platform or mobile app. Be sure to carefully research any investments you consider, and remember that investing involves risk.
Tips for Choosing a Brokerage
- Read reviews: Check out online reviews and compare different brokerages before making a decision.
- Consider your needs: Think about your investment goals, risk tolerance, and trading style. Choose a brokerage that aligns with your needs.
- Don’t be afraid to ask questions: Contact the brokerage’s customer service department if you have any questions about their services or fees.
Opening a brokerage account is a crucial step towards achieving your financial goals. By following these steps and choosing the right brokerage, you can confidently embark on your investment journey.
Developing a Diversified Investment Strategy
A diversified investment strategy is essential for any investor seeking to mitigate risk and maximize returns over the long term. By spreading your investments across different asset classes, sectors, and geographies, you can reduce the impact of any single investment’s performance on your overall portfolio.
A well-diversified portfolio should include a mix of assets that are not highly correlated with one another. This means that if one asset class is performing poorly, others are likely to be performing well, helping to offset losses and maintain a consistent return. Here are some key steps in developing a diversified investment strategy:
1. Define Your Investment Goals and Risk Tolerance
Before you start investing, it’s important to define your goals. What are you saving for? How much risk are you willing to take? Your goals and risk tolerance will determine the asset allocation strategy that is right for you. For instance, a young investor with a long investment horizon may be more comfortable with a higher proportion of stocks in their portfolio, while an older investor nearing retirement may prefer a more conservative portfolio with a higher allocation to bonds.
2. Choose the Right Asset Classes
There are many different asset classes to choose from, including stocks, bonds, real estate, commodities, and cash. Each asset class has its own risk and return profile. For instance, stocks typically offer higher returns than bonds but also carry higher risk. It’s important to choose a mix of asset classes that aligns with your risk tolerance and investment goals.
3. Consider Different Investment Strategies
Once you’ve chosen your asset classes, you need to decide how you want to invest in them. There are many different investment strategies, such as passive investing, active investing, and value investing. The best strategy for you will depend on your goals, risk tolerance, and investment knowledge.
4. Diversify Within Each Asset Class
It’s not enough to simply diversify across asset classes. You also need to diversify within each asset class. For example, if you’re investing in stocks, you should invest in a variety of industries, sectors, and company sizes. This will help to reduce the impact of any single company’s performance on your overall portfolio.
5. Monitor and Rebalance Your Portfolio
Once you’ve developed your diversified investment strategy, it’s important to monitor your portfolio and rebalance it regularly. Market conditions change over time, and your asset allocation may need to be adjusted to reflect these changes. Rebalancing ensures that your portfolio remains aligned with your goals and risk tolerance.
Building a diversified investment strategy requires careful planning and ongoing monitoring. By taking the time to develop a strategy that aligns with your goals and risk tolerance, you can increase your chances of achieving your financial objectives. It’s important to consult with a financial advisor for personalized guidance and support.
Investing Consistently Over Time
Investing consistently over time is a powerful strategy for achieving financial goals. It allows you to take advantage of the power of compounding, where your earnings generate further earnings, creating a snowball effect. By making regular contributions to your investments, you can steadily grow your wealth over the long term.
Benefits of Consistent Investing
There are several benefits to consistent investing:
- Compounding Returns: As your investments grow, the earnings generate further earnings, accelerating your wealth accumulation.
- Dollar-Cost Averaging: By investing a fixed amount regularly, you buy more shares when prices are low and fewer shares when prices are high, reducing average cost per share.
- Reduced Market Risk: Consistent investing helps to mitigate market volatility by averaging out price fluctuations over time.
- Financial Discipline: Making regular contributions encourages financial discipline and helps you build a strong financial foundation.
Strategies for Consistent Investing
Here are some strategies for consistent investing:
- Automate Your Investments: Set up automatic transfers from your checking account to your investment accounts.
- Establish a Regular Investment Schedule: Decide on a frequency (monthly, quarterly, annually) and stick to it.
- Use a Diversified Portfolio: Spread your investments across different asset classes (stocks, bonds, real estate) to reduce risk.
- Review and Adjust Regularly: Periodically review your investment strategy and make adjustments as needed to stay on track with your goals.
Conclusion
Consistent investing is a key pillar of building wealth over the long term. By committing to regular contributions and staying disciplined, you can unlock the power of compounding and achieve your financial aspirations. Remember to consult with a financial advisor for personalized guidance and to tailor your investment strategy to your individual needs.
Monitoring Your Investments and Rebalancing
Monitoring your investments and rebalancing your portfolio is crucial for achieving your financial goals. It allows you to stay on track, adjust your strategy as needed, and mitigate potential risks. Here’s a comprehensive guide to help you understand the importance of these practices and how to implement them effectively.
Why Monitor Your Investments?
Regularly monitoring your investments helps you stay informed about their performance and identify any potential issues early on. Here are some key reasons why monitoring is essential:
- Track Performance: Monitoring allows you to see how your investments are performing against your expectations and benchmark them against relevant market indices.
- Identify Risks: It helps you detect any emerging risks, such as declining asset values or changes in market conditions that could impact your portfolio.
- Adjust Your Strategy: Monitoring provides valuable insights that can inform adjustments to your investment strategy, such as rebalancing or shifting your asset allocation.
- Stay Disciplined: Regular monitoring can help you stay disciplined and avoid emotional reactions to market fluctuations.
Rebalancing Your Portfolio
Rebalancing involves adjusting your portfolio’s asset allocation to maintain your desired target percentages. Over time, the market values of different asset classes fluctuate, and your portfolio can drift from its original allocation. Rebalancing helps bring it back in line with your investment goals.
When to Rebalance
There’s no one-size-fits-all approach to rebalancing frequency. It depends on your investment goals, risk tolerance, and portfolio volatility. However, common rebalancing intervals include:
- Annually: This approach is suitable for most investors, as it allows for regular adjustments based on market movements.
- Semi-annually: This option provides more frequent monitoring and adjustments, especially for volatile portfolios.
- Quarterly: This approach is more suitable for investors with a high-risk tolerance or those actively managing their portfolios.
How to Rebalance
To rebalance your portfolio, you need to determine the current asset allocation and compare it to your target allocation. If any asset class has deviated significantly, you’ll need to sell some of the overperforming assets and buy more of the underperforming assets to bring the portfolio back in line with your target percentages.
Tips for Effective Monitoring and Rebalancing
Here are some practical tips to make monitoring and rebalancing more effective:
- Set Up Regular Review Schedules: Establish a regular schedule for reviewing your investments, whether it’s monthly, quarterly, or annually.
- Use Investment Tracking Tools: Utilize online platforms or financial software to track your portfolio performance and asset allocation.
- Stay Informed About Market Trends: Stay updated on market news, economic indicators, and industry trends that can affect your investments.
- Consult with a Financial Advisor: Consider seeking professional advice from a qualified financial advisor who can provide personalized guidance and support.
Conclusion
Monitoring your investments and rebalancing your portfolio are essential practices for long-term financial success. By staying informed, making timely adjustments, and staying disciplined, you can increase your chances of achieving your financial goals and navigating the complexities of the investment world.
The Power of Compound Growth for Long-Term Wealth
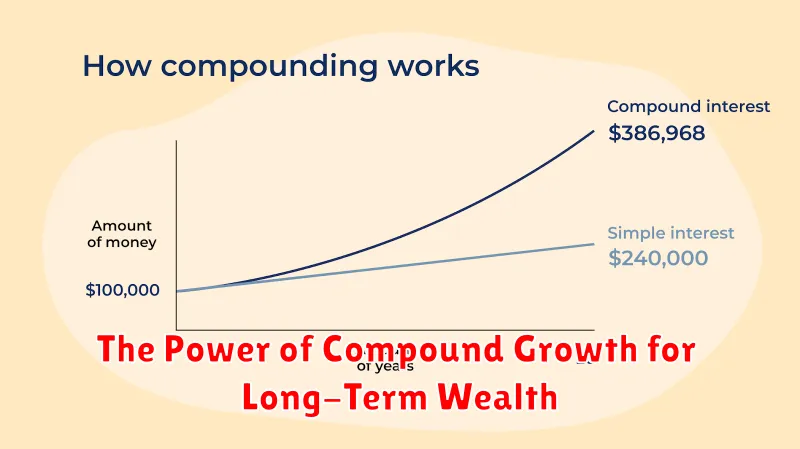
Compounding is a powerful concept in finance that describes the snowball effect of earning interest on both your principal investment and accumulated interest. It’s like a snowball rolling downhill, gathering more snow as it goes, and eventually becoming a massive ball. In the same way, your investments grow exponentially over time when you reinvest your earnings.
The earlier you start investing and the longer you let your money compound, the greater the potential for wealth accumulation. This is because the magic of compounding works best over long periods. Even small, consistent investments can grow significantly over time with the power of compounding.
Here’s how it works:
Imagine you invest $1,000 at a 10% annual return. After one year, you’ll earn $100 in interest, bringing your total to $1,100. The following year, you’ll earn 10% on $1,100, which is $110. This might seem like a small difference, but over time, the impact becomes massive.
After 30 years, your initial $1,000 investment would have grown to over $17,449.50! That’s the power of compounding at work. It’s not just about the initial investment, but about consistently reinvesting your earnings to generate even more growth.
Tips for maximizing compound growth:
- Start early: The earlier you start investing, the longer your money has to compound. Time is your most valuable asset.
- Invest regularly: Even small, consistent investments can add up over time. Try to invest a fixed amount regularly, like monthly or quarterly.
- Choose investments with a high return potential: While past performance is not indicative of future results, it’s important to choose investments that have historically delivered strong returns. Consider investing in diversified portfolios, such as mutual funds or ETFs.
- Minimize fees: High fees can eat into your returns and significantly impact the power of compounding. Choose investment vehicles with low fees and expenses.
- Be patient and stay disciplined: Compounding takes time, and it’s crucial to stay disciplined and avoid withdrawing your investments prematurely. Resist the temptation to panic sell during market downturns. Remember, the long-term growth potential of your investments is far greater than the short-term fluctuations.
Compounding is a powerful tool for building long-term wealth. By understanding the principles and applying these tips, you can harness the magic of compound growth to reach your financial goals.

