Are you looking to buy a house, consolidate debt, or finance a new car? Whatever your financial goals may be, chances are you’ll need to consider taking out a loan. But with so many different types of loans available, it can be overwhelming to know where to start. Understanding the various loan options and their associated terms is crucial for making informed financial decisions. This article will delve into the different types of loans commonly used for personal finance, exploring their benefits, drawbacks, and ideal situations.
From personal loans to home loans and auto loans, this comprehensive guide will provide you with a clear picture of the loan landscape. We’ll discuss the factors to consider when choosing a loan, such as interest rates, repayment terms, and eligibility criteria. By understanding these factors, you can confidently select the best loan for your unique financial needs, ensuring a smooth and successful borrowing experience.
Secured vs. Unsecured Loans: What’s the Difference?
When you’re looking for a loan, it’s important to understand the difference between secured and unsecured loans. This distinction affects everything from your interest rate to your chances of approval.
What is a Secured Loan?
A secured loan is a type of loan where the borrower pledges an asset as collateral. This collateral can be anything of value, such as a house, car, or savings account. If the borrower defaults on the loan, the lender can seize the collateral to recoup their losses.
What is an Unsecured Loan?
An unsecured loan, on the other hand, does not require any collateral. Instead, the lender assesses the borrower’s creditworthiness based on their credit history, income, and debt-to-income ratio. If the borrower defaults, the lender may have to take legal action to recover the money, but they cannot seize any assets.
Key Differences between Secured and Unsecured Loans
- Interest Rates: Secured loans typically have lower interest rates than unsecured loans because the lender has less risk. If the borrower defaults, the lender can seize the collateral.
- Loan Amounts: Secured loans often have higher loan limits than unsecured loans because the lender has a safety net in case of default.
- Approval Process: Secured loans may have a faster approval process than unsecured loans because the lender has less risk.
- Risk: Secured loans are typically considered less risky for lenders because the lender has collateral to recover if the borrower defaults.
Examples of Secured Loans
- Mortgages
- Auto Loans
- Home Equity Loans
Examples of Unsecured Loans
- Credit Cards
- Personal Loans
- Student Loans
Which Type of Loan is Right for You?
The best type of loan for you will depend on your individual circumstances. If you have good credit and need a large loan, a secured loan may be a good option. If you have less-than-perfect credit or need a smaller loan, an unsecured loan may be a better choice.
Before you apply for any type of loan, it’s important to shop around and compare interest rates and terms from different lenders. You should also read the loan agreement carefully to make sure you understand the terms and conditions.
Personal Loans: Uses, Pros, and Cons
A personal loan is a type of unsecured loan that you can use for a variety of purposes, such as debt consolidation, home improvement, medical expenses, or even a vacation. Unlike secured loans, which require collateral, personal loans are based on your creditworthiness. This means that the lender will assess your credit score, income, and debt-to-income ratio to determine whether or not to approve your loan and at what interest rate.
Uses of Personal Loans
Personal loans can be used for a variety of purposes, but some of the most common uses include:
- Debt consolidation: You can use a personal loan to consolidate high-interest debt, such as credit card debt, into one lower-interest loan. This can help you save money on interest and simplify your monthly payments.
- Home improvement: Personal loans can be used to finance home improvements, such as a new roof, kitchen remodel, or bathroom upgrade.
- Medical expenses: If you have unexpected medical expenses, a personal loan can help you cover the costs.
- Major purchases: Personal loans can be used to finance major purchases, such as a new car, furniture, or appliances.
- Vacation: If you’re planning a dream vacation, a personal loan can help you make it a reality.
Pros of Personal Loans
There are several advantages to taking out a personal loan, including:
- Fixed interest rates: Most personal loans have fixed interest rates, which means that your monthly payment will stay the same for the life of the loan. This can help you budget more effectively.
- Flexible repayment terms: Personal loans typically have flexible repayment terms, so you can choose a term that fits your budget.
- Quick and easy application process: Applying for a personal loan is generally quick and easy, and you may be able to receive your funds within a few days.
- No collateral required: As mentioned above, personal loans are unsecured, which means you don’t need to put up any collateral to get approved.
- Can help improve your credit score: If you make your payments on time, a personal loan can help improve your credit score.
Cons of Personal Loans
While personal loans offer several benefits, there are also some drawbacks to consider:
- High interest rates: Personal loans can have high interest rates, especially if you have a lower credit score. It is important to shop around and compare rates from different lenders before you choose a loan.
- Origination fees: Some lenders charge origination fees when you take out a personal loan. These fees can add to the total cost of the loan.
- Can lead to debt if not used responsibly: Like any type of loan, if you don’t manage your payments responsibly, a personal loan can lead to debt. Make sure you have a plan in place to repay the loan before you take it out.
Conclusion
A personal loan can be a good option for financing a variety of needs. However, it’s important to weigh the pros and cons carefully before you decide if a personal loan is right for you. You should also shop around and compare rates from different lenders to get the best deal.
Auto Loans: Navigating Financing Options

Purchasing a car is a significant financial decision, and securing an auto loan is often a crucial step in the process. With various financing options available, it can be overwhelming to determine the best path for your individual needs. This guide will provide a comprehensive overview of auto loans, exploring different types of loans, factors influencing interest rates, and tips for securing the most favorable financing terms.
Types of Auto Loans
Auto loans primarily fall into two categories: new car loans and used car loans. While the fundamental principles are similar, some key distinctions exist.
New Car Loans
New car loans are specifically designed for financing brand-new vehicles directly from dealerships. These loans often come with lower interest rates than used car loans due to the perceived lower risk associated with new cars. However, new cars typically depreciate faster, meaning the loan amount may exceed the vehicle’s actual value sooner.
Used Car Loans
Used car loans cater to the purchase of previously owned vehicles. These loans typically carry higher interest rates due to the increased uncertainty surrounding the car’s condition and potential for future repairs. However, used cars offer significant cost savings compared to their new counterparts.
Factors Influencing Interest Rates
The interest rate on your auto loan is a crucial factor determining the total cost of borrowing. Several factors influence the interest rate you qualify for, including:
- Credit Score: Your credit score is the primary factor determining your interest rate. A higher credit score typically translates to lower interest rates.
- Loan Term: Longer loan terms generally result in lower monthly payments but can lead to higher overall interest costs due to more time for interest to accrue.
- Loan Amount: Larger loan amounts often come with higher interest rates due to the increased risk for the lender.
- Vehicle Type: Certain vehicle types, such as luxury cars, might attract higher interest rates.
- Lender: Different lenders have varying interest rate policies and may offer different terms based on their risk assessment.
Securing Favorable Financing Terms
To secure the most advantageous financing terms, consider these tips:
- Improve Your Credit Score: A higher credit score significantly improves your chances of qualifying for lower interest rates.
- Shop Around for Rates: Compare offers from multiple lenders to find the best interest rate and loan terms.
- Negotiate the Interest Rate: Don’t be afraid to negotiate with lenders to try and secure a lower interest rate.
- Consider a Shorter Loan Term: While higher monthly payments, a shorter loan term can significantly reduce overall interest costs.
- Explore Loan Options: Consider different types of auto loans, such as secured loans or loans with a co-signer, to see if they offer more favorable terms.
Conclusion
Navigating the complexities of auto loans requires thorough research and careful consideration. By understanding different loan types, factors influencing interest rates, and strategies for securing favorable financing terms, you can make an informed decision that aligns with your financial goals. Remember, a well-structured auto loan can be a valuable tool for acquiring a vehicle while minimizing the overall cost of borrowing.
Mortgage Loans: Choosing the Right Type

A mortgage loan is a secured loan that is used to finance the purchase of a home or other real estate. The loan is secured by the property itself, which means that the lender can foreclose on the property if the borrower defaults on the loan. Mortgages are a long-term debt, typically lasting for 15 or 30 years.
There are many different types of mortgage loans available, each with its own terms and conditions. It is important to understand the different types of loans and their features before you apply for a mortgage.
Types of Mortgage Loans
Here are some of the most common types of mortgage loans:
- Fixed-rate mortgage: This type of loan has a fixed interest rate for the entire term of the loan. This means that your monthly payments will remain the same for the life of the loan. Fixed-rate mortgages are a good option for borrowers who want predictable monthly payments and who are concerned about rising interest rates.
- Adjustable-rate mortgage (ARM): This type of loan has an interest rate that can change over time. ARMs typically have a lower initial interest rate than fixed-rate mortgages, but the rate can adjust upward after a certain period of time. ARMs can be a good option for borrowers who plan to sell their home before the interest rate adjusts or who are willing to accept the risk of higher payments in the future.
- FHA loan: This type of loan is insured by the Federal Housing Administration (FHA). FHA loans have lower down payment requirements and less stringent credit requirements than conventional loans. They are a good option for borrowers who have a lower credit score or who are unable to make a large down payment.
- VA loan: This type of loan is guaranteed by the Department of Veterans Affairs (VA). VA loans are available to eligible veterans, active-duty military personnel, and surviving spouses. They have no down payment requirement and have lower interest rates than conventional loans. VA loans are a good option for eligible borrowers who want a loan with favorable terms.
- USDA loan: This type of loan is guaranteed by the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA). USDA loans are available to borrowers who live in eligible rural areas. They have low down payment requirements and low interest rates. USDA loans are a good option for borrowers who want to buy a home in a rural area and who qualify for the program.
Choosing the Right Type of Loan
The best type of mortgage loan for you will depend on your individual circumstances, including your credit score, your down payment amount, your financial goals, and your risk tolerance.
Here are some factors to consider when choosing a mortgage loan:
- Interest rate: The interest rate will determine your monthly payments and the total cost of your loan. A lower interest rate will result in lower monthly payments and a lower total cost of the loan.
- Loan term: The loan term is the length of time you have to repay the loan. A shorter loan term will result in higher monthly payments but a lower total cost of the loan. A longer loan term will result in lower monthly payments but a higher total cost of the loan.
- Down payment: The down payment is the amount of money you pay upfront to purchase the home. A larger down payment will result in a lower loan amount and a lower monthly payment. A smaller down payment will result in a higher loan amount and a higher monthly payment.
- Closing costs: Closing costs are the fees associated with the purchase of a home. These fees can include things like appraisal fees, loan origination fees, and title insurance.
- Your financial situation: Your financial situation will determine how much of a mortgage you can afford. Consider your income, expenses, and debt-to-income ratio when determining how much you can borrow.
It is important to shop around for the best mortgage rate and terms. You should contact multiple lenders and compare their rates and fees. You can also use an online mortgage calculator to estimate your monthly payments and the total cost of the loan. It is also a good idea to speak with a mortgage broker, who can help you find the best loan for your needs.
Choosing the right mortgage loan can be a complicated process. It is important to do your research and compare your options before you apply for a loan. By understanding the different types of loans and their features, you can make an informed decision about which loan is right for you.
Student Loans: Understanding Repayment Options

Navigating the world of student loans can feel overwhelming, especially when it comes to repayment. With various repayment plans and options available, choosing the right one can be confusing. This guide will provide a clear understanding of the different repayment options available to you, empowering you to make informed decisions about your student loan debt.
Standard Repayment Plan
The Standard Repayment Plan is the most common repayment option. It’s a fixed monthly payment spread over 10 years, based on the total amount of your loans. While this plan offers a shorter repayment period, it may result in higher monthly payments compared to other options.
Graduated Repayment Plan
The Graduated Repayment Plan provides lower initial payments that gradually increase over the course of the 10-year repayment term. This can be a good option for borrowers who anticipate their income to increase over time.
Extended Repayment Plan
If you need more time to repay your loans, the Extended Repayment Plan allows you to spread payments over 25 years. This plan may be beneficial if you have a large loan balance or a low income, but it will likely result in higher interest charges over the longer repayment period.
Income-Driven Repayment (IDR) Plans
Income-Driven Repayment (IDR) Plans are designed to make monthly payments more affordable by tying them to your income. There are several IDR plans available, such as:
- Income-Based Repayment (IBR)
- Pay As You Earn (PAYE)
- Revised Pay As You Earn (REPAYE)
These plans typically cap your monthly payments at a percentage of your discretionary income and may result in loan forgiveness after 20 or 25 years.
Public Service Loan Forgiveness (PSLF)
If you work for a qualifying public service organization, the Public Service Loan Forgiveness (PSLF) program allows you to have the remaining balance of your federal student loans forgiven after making 120 qualifying payments. However, it’s crucial to carefully review the eligibility requirements and make sure you’re enrolled in an IDR plan to qualify.
Choosing the Right Option
The best repayment option for you depends on your individual circumstances, including your income, loan balance, and future financial goals. It’s recommended to carefully consider your options, explore your eligibility for different plans, and consult with a financial advisor to make an informed decision.
Payday Loans: Proceed with Caution
Payday loans, also known as cash advance loans, are short-term, high-interest loans that are typically due on your next payday. They can be a tempting option when you need cash quickly, but they come with a lot of risks. If you’re considering taking out a payday loan, it’s important to understand the potential consequences.
High Interest Rates
The biggest drawback of payday loans is their extremely high interest rates. The average payday loan APR (annual percentage rate) is around 400%, but some lenders charge even more. This means that if you borrow $100 and pay it back within two weeks, you could end up owing more than $150.
Debt Cycle
If you’re unable to repay the loan in full on your next payday, you may be able to roll it over into a new loan. This can create a vicious cycle of debt, as you’ll continue to accrue interest and fees. It’s very easy to get stuck in a debt trap with payday loans.
Impact on Credit Score
Payday loans can negatively impact your credit score. Many lenders report your loan activity to the credit bureaus, so a missed payment or a history of borrowing could damage your credit.
Alternatives to Payday Loans
Before you take out a payday loan, consider alternatives that might be better for your financial situation. These include:
- Borrowing from friends or family: This can be a cheaper option than a payday loan, but it’s important to be upfront about your repayment plans and to make sure everyone involved is comfortable with the arrangement.
- Using a credit card: Credit cards typically have lower interest rates than payday loans. However, it’s important to use your credit card responsibly and to avoid overspending.
- Getting a personal loan: Personal loans have fixed interest rates and repayment terms, which can be more predictable than payday loans. You may be able to get a personal loan from a bank, credit union, or online lender.
- Exploring options at your local community center: There may be resources available to help you manage your finances or find other ways to get the money you need.
Conclusion
Payday loans can be a risky option, and you should only consider them as a last resort. If you do decide to take out a payday loan, be sure to shop around for the best rates and terms, and make a plan to repay the loan in full as soon as possible.
Home Equity Loans: Tapping into Your Home’s Value
A home equity loan, also known as a second mortgage, allows homeowners to borrow money against the equity they’ve built up in their homes. Equity is the difference between the current market value of your home and the amount you still owe on your mortgage. For example, if your home is worth $300,000 and you have a mortgage balance of $150,000, you have $150,000 in equity.
Home equity loans can be a valuable tool for homeowners who need access to funds for a variety of purposes, such as:
- Home improvements
- Debt consolidation
- Medical expenses
- Education costs
- Major purchases
How Home Equity Loans Work
When you take out a home equity loan, you’ll receive a lump sum of money that you can use as you see fit. You’ll then repay the loan over a fixed period of time, typically 5 to 30 years, with regular monthly payments. The interest rate on a home equity loan is typically lower than the interest rate on a personal loan or credit card, but higher than the rate on your first mortgage.
Advantages of Home Equity Loans
- Lower interest rates than other types of loans.
- Fixed monthly payments, making budgeting easier.
- Tax-deductible interest for home improvements.
- Access to a large sum of money for significant needs.
Disadvantages of Home Equity Loans
- Risk of losing your home if you default on the loan.
- Higher interest rates than your first mortgage.
- Closing costs can be substantial.
- Limited access to funds if you have a small amount of equity.
Alternatives to Home Equity Loans
If you’re considering a home equity loan, it’s important to explore other financing options that may be better suited to your needs. These include:
- Personal loans: Offer quick and easy access to funds, but typically come with higher interest rates.
- Credit cards: Useful for smaller expenses, but can have high interest rates and variable payments.
- Home equity lines of credit (HELOCs): Allow you to borrow funds as needed, but interest rates can be variable.
Conclusion
A home equity loan can be a helpful financial tool, but it’s important to weigh the pros and cons carefully before taking out a loan. By understanding the risks and benefits involved, you can make an informed decision that meets your financial goals.
Comparing Loan Terms and Interest Rates
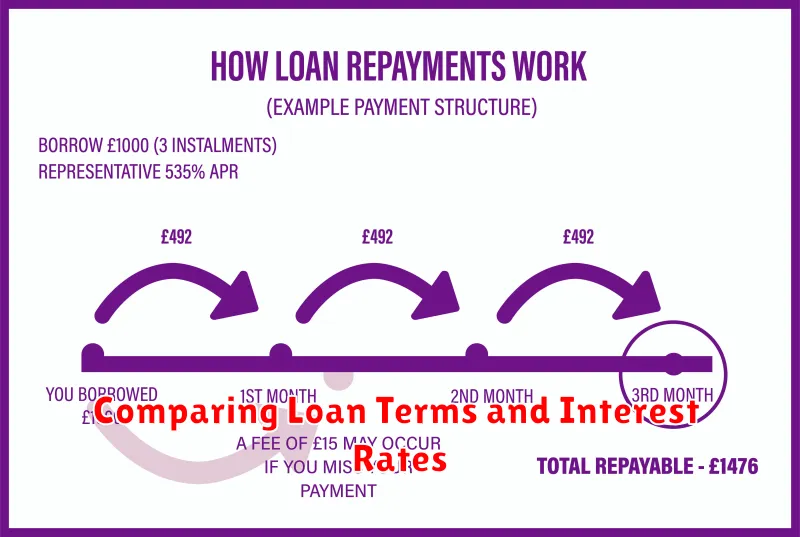
When you’re looking for a loan, it’s important to compare loan terms and interest rates. These factors will determine how much you’ll pay in total over the life of the loan.
Loan terms refer to the length of time you have to repay the loan. A longer loan term will typically result in lower monthly payments, but you’ll pay more interest over the life of the loan. A shorter loan term will have higher monthly payments, but you’ll pay less interest overall.
Interest rates are the percentage charged on the amount of money you borrow. A lower interest rate will result in lower overall costs. Interest rates can vary depending on your credit score, the type of loan, and the lender.
Here are some tips for comparing loan terms and interest rates:
- Shop around with multiple lenders to get the best rates.
- Consider the total cost of the loan, including interest and fees.
- Choose a loan term that fits your budget and financial goals.
- Read the loan documents carefully before signing anything.
By comparing loan terms and interest rates, you can get the best possible loan for your needs. This can save you money in the long run.

