Retirement. It’s something that everyone plans for but no one really thinks about until it’s just around the corner. And when you do start thinking about it, the idea can feel overwhelming. After all, how do you know how much you need to save? What if you don’t have enough? What if you save too much? And then there’s the question of what you’ll even do with all that free time!
The good news is that you don’t have to go it alone. There are plenty of resources available to help you figure out how much you need to save for retirement. And once you have a plan, you can start putting your money to work for you. With a little planning and effort, you can enjoy a comfortable and secure retirement. Read on to learn how much you need to save and some tips on how to get started.
Factors Influencing Your Retirement Savings Needs
Retirement planning is a crucial aspect of financial well-being, ensuring a comfortable and secure future. However, determining the right amount of retirement savings can be daunting, as numerous factors come into play. Understanding these factors is essential for making informed decisions and achieving your retirement goals.
1. Lifestyle Expectations
Your desired lifestyle in retirement plays a significant role in determining your savings needs. Consider factors such as your preferred living location, travel plans, hobbies, and entertainment expenses. If you envision an active and luxurious retirement, your savings requirements will be higher compared to a modest and simple lifestyle.
2. Retirement Age
The age at which you plan to retire has a direct impact on your savings needs. Retiring earlier will require a larger nest egg to cover a longer period. Conversely, retiring later will allow you to accumulate more savings and potentially draw on Social Security benefits for a shorter duration.
3. Life Expectancy
Your life expectancy is crucial in retirement planning. Consulting with a financial advisor can help you estimate your life expectancy and adjust your savings accordingly. A longer life expectancy demands a larger retirement fund to ensure financial security throughout your golden years.
4. Healthcare Costs
Healthcare expenses are a significant consideration in retirement. As you age, medical needs can increase, leading to higher healthcare costs. Factor in the rising costs of health insurance premiums, prescription drugs, and potential long-term care.
5. Inflation
Inflation erodes the purchasing power of your savings over time. Consider the projected inflation rate and adjust your savings goals accordingly. A higher inflation rate will necessitate a larger retirement fund to maintain the same standard of living.
6. Investment Returns
The expected returns on your investments are crucial in retirement planning. Conservative estimates of investment returns are essential to avoid overestimating your savings potential. Consider the risks associated with different investment options and choose strategies that align with your risk tolerance.
7. Social Security Benefits
Social Security benefits can provide a valuable source of income in retirement, but it’s essential to understand how they will contribute to your overall financial plan. Factor in your expected Social Security benefits when determining your savings needs. Keep in mind that Social Security alone is unlikely to cover all your retirement expenses.
8. Existing Debt
Existing debt, such as mortgage payments, student loans, or credit card balances, can significantly impact your retirement savings. Aim to pay down debt before or during retirement to free up more funds for living expenses.
9. Unexpected Expenses
Unforeseen expenses can arise in retirement, such as home repairs, medical emergencies, or assisting family members. Building a contingency fund within your retirement savings can provide financial cushion for unexpected events.
10. Taxes
Retirement income, such as withdrawals from 401(k)s or IRAs, is generally subject to taxation. Factor in potential tax liabilities when determining your savings needs and consider tax-advantaged retirement accounts to minimize your tax burden.
Conclusion
Determining your retirement savings needs is a complex process that requires careful consideration of various factors. Consulting with a financial advisor can provide personalized guidance and help you develop a comprehensive retirement plan. By understanding these factors and taking proactive steps, you can increase your chances of achieving financial security and enjoying a comfortable retirement.
Estimating Your Retirement Expenses
Retirement is a significant life milestone, and it’s crucial to ensure you have enough financial resources to live comfortably during your golden years. One of the most critical steps in planning for retirement is accurately estimating your expenses.
Here’s a comprehensive guide to help you estimate your retirement expenses effectively:
1. Analyze Your Current Spending Habits
Start by taking a close look at your current spending patterns. Track your expenses for several months, categorizing them into essential needs like housing, food, healthcare, and transportation, and discretionary items like entertainment, travel, and dining out. This exercise will give you a realistic baseline for your future spending habits.
2. Account for Inflation
Inflation can significantly impact your retirement expenses. The cost of goods and services tends to rise over time, so it’s essential to factor in inflation when estimating your future needs. You can use online inflation calculators to project how your expenses might increase over the years.
3. Consider Lifestyle Changes
Retirement often brings about lifestyle changes. You might travel more, pursue hobbies, or spend more time with family and friends. These changes can impact your spending. Consider how your lifestyle might evolve in retirement and factor those adjustments into your estimates.
4. Healthcare Expenses
Healthcare costs are a significant consideration in retirement. As you age, your healthcare needs may increase. Factor in potential medical expenses, including deductibles, copayments, and prescription drugs. Remember that Medicare may cover some costs, but you may still need supplemental insurance.
5. Housing Costs
Housing is often the largest expense in retirement. Will you downsize your home, move to a different location, or stay in your current residence? Consider property taxes, insurance, maintenance, and potential mortgage payments.
6. Emergency Fund
It’s wise to have an emergency fund for unforeseen expenses in retirement. Allocate a portion of your estimated expenses for unexpected events such as car repairs, medical emergencies, or home repairs. A well-funded emergency fund can provide peace of mind.
7. Retirement Planning Tools
Utilize online retirement calculators and financial planning tools to help you estimate your expenses and project your financial needs. These tools can provide valuable insights and help you make informed decisions about your retirement savings goals.
8. Seek Professional Advice
Consider consulting with a financial advisor who specializes in retirement planning. They can provide personalized guidance, help you refine your estimates, and develop a comprehensive financial plan tailored to your specific needs and goals.
Estimating your retirement expenses is a critical step in planning for a secure and comfortable retirement. By carefully analyzing your current spending habits, accounting for inflation and lifestyle changes, and utilizing available resources, you can develop a realistic and effective plan to ensure your financial well-being in your golden years.
Determining Your Retirement Income Sources
Retirement is a significant life transition that requires careful planning and preparation. One crucial aspect of this preparation is understanding and securing your income sources during retirement. This article will guide you through the process of determining your retirement income sources, ensuring a comfortable and financially secure future.
1. Assess Your Current Financial Situation
Start by taking stock of your current financial situation. This includes:
- Savings and Investments: Evaluate your current retirement savings, including 401(k)s, IRAs, and other investment accounts.
- Debt: Assess any outstanding debts, such as mortgages, loans, or credit card balances. These can impact your retirement income needs.
- Income: Review your current income sources, including salary, investments, and any other sources of revenue.
- Expenses: Analyze your current monthly expenses, including housing, utilities, transportation, food, and entertainment. Identify any unnecessary expenses that can be reduced or eliminated.
2. Determine Your Retirement Income Needs
Once you have a clear picture of your current finances, you can project your future income needs. Consider the following factors:
- Lifestyle: How do you envision your retirement lifestyle? Will you travel extensively, pursue hobbies, or engage in volunteer work? These activities will impact your expenses.
- Healthcare: Healthcare costs can rise significantly in retirement. Factor in potential medical expenses, long-term care, and insurance premiums.
- Inflation: Inflation can erode the purchasing power of your savings. Factor in an inflation rate to ensure your retirement income keeps pace with rising costs.
- Longevity: Life expectancy is increasing, so you need to plan for a longer retirement. You may need to save more to cover your expenses for a longer period.
3. Explore Your Retirement Income Sources
With a clear understanding of your financial situation and retirement income needs, you can explore various income sources:
- Social Security: Social Security is a government-funded retirement program that provides monthly benefits based on your earnings history.
- Employer-Sponsored Retirement Plans: Many employers offer retirement plans, such as 401(k)s, that allow you to save pre-tax income for retirement.
- Individual Retirement Accounts (IRAs): IRAs are retirement savings accounts that individuals can open to save for retirement.
- Annuities: Annuities are financial products that provide a stream of income during retirement, often guaranteed for life.
- Part-Time Work: If you enjoy working, you can supplement your income with part-time jobs during retirement.
- Investments: Investing in stocks, bonds, or real estate can provide additional income during retirement.
4. Create a Retirement Income Plan
Once you’ve identified your potential income sources, create a comprehensive retirement income plan. This plan should include:
- Income projections: Estimate your income from each source, taking into account growth and potential inflation.
- Expense projections: Estimate your projected monthly expenses during retirement.
- Withdrawal strategy: Determine how you will withdraw money from your savings and investments during retirement.
- Contingency plans: Plan for potential unexpected events, such as market downturns or health emergencies.
5. Regularly Review and Adjust Your Plan
Your retirement income plan should not be set in stone. Regularly review and adjust your plan based on changes in your circumstances, market conditions, and income needs. By staying proactive and making necessary adjustments, you can ensure a secure and comfortable retirement.
Determining your retirement income sources requires careful consideration of your current financial situation, future income needs, and available options. By following the steps outlined in this article, you can develop a comprehensive retirement income plan that provides financial security and peace of mind during your golden years.
Calculating Your Retirement Savings Goal
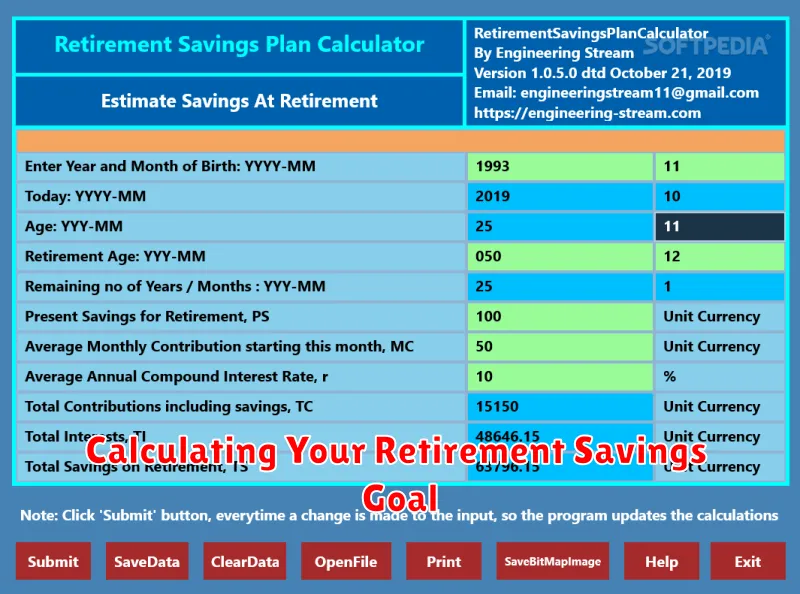
Retirement is a time for relaxation and enjoying the fruits of your labor. It’s a period where you can finally focus on your hobbies, travel, and spend time with loved ones. But to enjoy a comfortable and secure retirement, it’s crucial to plan ahead and calculate your retirement savings goal. This goal should be a target that ensures you have enough financial resources to cover your expenses throughout your golden years.
To determine your retirement savings goal, consider the following factors:
- Desired Lifestyle: What kind of lifestyle do you envision in retirement? Are you planning to travel extensively, pursue expensive hobbies, or simply live modestly?
- Retirement Duration: How long do you expect to live in retirement? This will influence the amount of money you need to save.
- Expected Expenses: Make a realistic estimate of your monthly expenses in retirement, including housing, healthcare, food, utilities, and entertainment.
- Inflation: Consider the impact of inflation on your expenses. Remember that the cost of living is likely to increase over time, so factor that in your calculations.
- Investment Returns: While you can’t guarantee investment returns, it’s important to have a reasonable expectation. Research historical average returns and factor them into your calculations.
- Social Security Benefits: If you’re eligible for Social Security, factor in your projected benefits. However, don’t rely solely on Social Security, as it’s likely to cover only a portion of your retirement expenses.
There are several online calculators and tools available to help you determine your retirement savings goal. These tools typically require you to input your personal information, including your age, current savings, desired retirement age, expected expenses, and estimated investment returns. The calculator will then generate an estimated retirement savings goal based on your inputs.
Remember that your retirement savings goal is a dynamic number that may need adjustments over time. As your circumstances change, such as changes in your income, expenses, or investment returns, you should re-evaluate and adjust your savings goal accordingly. It’s also wise to consult with a financial advisor who can provide personalized guidance and create a comprehensive retirement plan tailored to your specific needs.
Retirement Savings Strategies at Different Ages
Retirement planning is a lifelong endeavor, and the strategies you employ will change as you age. From your 20s to your 60s, each decade presents unique opportunities and challenges for building a secure financial future. Here’s a breakdown of retirement savings strategies tailored to different ages:
Your 20s: Building a Foundation
Your 20s are the perfect time to start saving, even if it’s just a small amount. The power of compounding works in your favor, allowing your investments to grow significantly over time. Consider these strategies:
- Maximize contributions to a 401(k) or Roth IRA: These tax-advantaged accounts allow you to save for retirement with pre-tax or tax-free withdrawals in retirement.
- Take advantage of employer matching: If your employer offers a 401(k) match, be sure to contribute enough to receive the full match. This is essentially free money you’re leaving on the table.
- Start a Roth IRA if you’re eligible: Roth IRAs allow you to contribute after-tax dollars, but withdrawals in retirement are tax-free.
- Invest in low-cost index funds: Index funds track a specific market index, providing diversification and low fees.
Your 30s: Increasing Contributions and Focusing on Debt
Your 30s are a time of increased financial responsibility, with potential family commitments and homeownership. Focus on boosting your savings and managing debt:
- Increase your retirement contributions: As your income grows, aim to increase your 401(k) or IRA contributions.
- Pay off high-interest debt: Debt payments can eat into your savings. Prioritize paying off credit card debt and other high-interest loans.
- Revisit your investment portfolio: Adjust your investment strategy based on your risk tolerance and time horizon. You may want to consider increasing your stock exposure as your investment time frame lengthens.
Your 40s: Saving for a Comfortable Retirement
By your 40s, you’ve likely established a strong financial foundation. Now, it’s time to focus on maximizing your savings to ensure a comfortable retirement:
- Contribute the maximum to your 401(k) or IRA: Take advantage of the maximum allowable contribution limits for your retirement accounts.
- Consider a Roth conversion ladder: This strategy allows you to convert traditional IRA funds to a Roth IRA, potentially reducing your tax burden in retirement.
- Explore other retirement savings options: Look into options like a Health Savings Account (HSA) or a Solo 401(k) if they’re appropriate for your situation.
Your 50s: Planning for the Future
As you approach retirement, it’s crucial to refine your plans and ensure you’re on track to meet your financial goals:
- Review your retirement projections: Use online calculators or consult with a financial advisor to estimate your retirement income needs.
- Develop a withdrawal strategy: Plan how you’ll access your retirement funds and manage your income in retirement.
- Consider downsizing or relocating: If you’re open to it, moving to a smaller home or a more affordable location can help reduce expenses in retirement.
Your 60s: Transitioning to Retirement
This is the decade where your retirement dreams become reality. Focus on managing your assets wisely and enjoying your well-deserved time off:
- Begin taking distributions from your retirement accounts: Start drawing on your savings to cover your expenses.
- Adjust your investment strategy: As you transition to retirement, you may want to shift your portfolio toward lower-risk investments.
- Stay informed about tax implications: Be aware of the tax implications of withdrawals from retirement accounts.
Remember, retirement planning is a journey, not a destination. By starting early, contributing regularly, and making smart decisions, you can create a secure financial future and enjoy a comfortable retirement.
Choosing the Right Retirement Accounts
Saving for retirement is crucial, but it can be overwhelming to navigate the different retirement accounts available. Understanding the nuances of each account can help you make informed decisions for your financial future. Here’s a guide to some popular retirement accounts:
401(k)
A 401(k) is a retirement savings plan offered by your employer. It allows you to contribute pre-tax dollars to the plan, which grows tax-deferred. Some employers may even offer a matching contribution, essentially giving you free money! This is a fantastic way to build your retirement nest egg.
Traditional IRA
A Traditional IRA is a retirement account you can open on your own, regardless of whether you have an employer-sponsored plan. Like a 401(k), your contributions are tax-deductible, and your earnings grow tax-deferred. You’ll pay taxes on withdrawals in retirement.
Roth IRA
A Roth IRA is similar to a Traditional IRA, but the key difference is that your contributions are made with after-tax dollars. This means your withdrawals in retirement are tax-free. This can be advantageous for those who expect to be in a higher tax bracket in retirement.
Choosing the Right Account
The best retirement account for you depends on your individual circumstances, such as your income, tax bracket, and employer contributions. Here are some things to consider:
- Employer matching: If your employer offers a matching contribution to your 401(k), you’ll want to take advantage of this free money.
- Tax implications: Consider your current tax bracket and your expected tax bracket in retirement. If you anticipate being in a higher bracket, a Roth IRA might be a better choice.
- Investment options: Some accounts offer a wider range of investment options than others.
- Contribution limits: Each account has annual contribution limits. Be sure to factor this into your savings strategy.
Final Thoughts
Don’t delay in starting your retirement savings journey. It’s never too early or too late to start planning for your future. Take advantage of the resources available to you, including financial advisors and online tools, to help you make informed decisions. Remember, the key is to start saving and to be consistent over time.
Adjusting Your Savings Plan Over Time

Saving money is a crucial aspect of achieving financial security and reaching your financial goals. While it’s important to have a savings plan, it’s equally important to regularly assess and adjust it as your life changes and circumstances evolve. This is because what works for you now might not be as effective in the future. Here are some key factors to consider when adjusting your savings plan over time:
1. Income Changes
Your income will likely fluctuate throughout your life. Promotions, salary increases, or career changes can boost your income, while periods of unemployment or reduced work hours can decrease it. When your income changes, it’s essential to review your savings plan and make adjustments accordingly. If your income rises, you can consider increasing your savings contributions to reach your goals faster. Conversely, if your income decreases, you might need to temporarily reduce your savings contributions or re-evaluate your goals to align with your new financial reality.
2. Lifestyle Changes
Life is full of unexpected twists and turns that can impact your savings plan. Major life events like marriage, having children, buying a home, or retirement can significantly alter your financial needs and priorities. For instance, starting a family often increases expenses for childcare, education, and housing. In such situations, you may need to adjust your savings plan by prioritizing certain goals or reducing spending in other areas to accommodate the increased expenses.
3. Inflation
Inflation is the steady increase in the prices of goods and services over time. It erodes the purchasing power of your savings, meaning that your money won’t go as far in the future as it does today. To combat inflation, you may need to increase your savings contributions to maintain the real value of your savings. Consider adjusting your savings plan to outpace inflation and ensure that your money continues to grow over time.
4. Investment Performance
The performance of your investments can also influence your savings plan. If your investments are performing well, you might consider reducing your savings contributions or increasing your investment allocations to potentially grow your wealth faster. On the other hand, if your investments are performing poorly, you may need to reassess your investment strategy, diversify your portfolio, or consider increasing your savings contributions to compensate for any losses.
5. Financial Goals
Your financial goals can change over time, leading to adjustments in your savings plan. You may have different priorities at various stages of your life, such as saving for a down payment on a house, funding your children’s education, or planning for a comfortable retirement. When your goals change, ensure that your savings plan aligns with your new priorities. If you have a new financial goal, create a dedicated savings plan to reach it, and adjust your existing savings plan accordingly.
6. Emergency Fund
An emergency fund is a critical component of any savings plan. It acts as a safety net to cover unexpected expenses, such as medical bills, car repairs, or job loss. Your emergency fund should be reviewed and adjusted as your financial situation changes. If you experience a significant income reduction or increased expenses, you might need to increase your emergency fund to ensure you have enough to cover unexpected events. Conversely, if your income increases or your expenses decrease, you can consider increasing your savings contributions to your emergency fund.
7. Regular Review
It’s highly recommended to regularly review your savings plan, at least annually, but ideally every six months, to ensure it aligns with your current financial situation and goals. This review will help you identify areas where you can make improvements, such as increasing your contributions, adjusting your investment allocation, or revising your financial goals. This proactive approach will help you stay on track with your savings goals and achieve financial success.
Seeking Professional Financial Advice for Retirement Planning
Retirement planning is a crucial aspect of securing your financial future. As you approach retirement, it is essential to have a comprehensive plan that addresses your financial goals, income sources, and expenses. Seeking professional financial advice can provide valuable guidance and support throughout this process.
Benefits of Professional Financial Advice
A qualified financial advisor can offer numerous benefits, including:
- Personalized Financial Plan: Financial advisors work with you to create a customized plan tailored to your unique circumstances, including your risk tolerance, investment goals, and retirement timeline.
- Investment Guidance: They provide expert insights on asset allocation, investment strategies, and portfolio diversification to help you grow your savings and achieve your financial objectives.
- Retirement Income Strategies: Financial advisors can help you develop strategies for generating income in retirement, such as Social Security planning, pension management, and retirement account withdrawals.
- Tax Optimization: They can advise on tax-efficient investment strategies and retirement planning strategies to minimize your tax burden.
- Financial Education: Financial advisors educate you on key financial concepts, empowering you to make informed decisions about your finances.
Finding the Right Financial Advisor
When choosing a financial advisor, it is crucial to consider the following factors:
- Credentials and Experience: Look for advisors with relevant certifications, such as a Certified Financial Planner (CFP®) or a Chartered Financial Analyst (CFA®), and extensive experience in retirement planning.
- Fees and Compensation: Understand the advisor’s fee structure, whether it’s hourly, commission-based, or a flat fee. Consider the cost versus the value they provide.
- Communication Style: Choose an advisor who is communicative, transparent, and easy to understand. They should explain financial concepts clearly and be responsive to your questions.
- References and Reviews: Seek recommendations from trusted sources and research the advisor’s reputation online.
Conclusion
Seeking professional financial advice for retirement planning can be a wise decision. A qualified advisor can provide invaluable support, guidance, and expertise to help you achieve your financial goals and enjoy a secure and comfortable retirement.

