Are you tired of watching your savings dwindle away due to inflation? Are you looking for a way to grow your wealth without taking on excessive risk? If so, then you need to learn about dividend investing. Dividend investing is a strategy where you buy stocks in companies that pay out a portion of their profits to shareholders in the form of dividends. This can be a powerful way to build wealth over time, as you can receive regular income from your investments while also benefiting from potential stock price appreciation.
Dividend investing is a popular strategy among investors of all experience levels because it offers a number of benefits. First, it allows you to generate passive income from your investments. Second, it can help you to diversify your portfolio and reduce your overall risk. And third, it can be a great way to build long-term wealth. In this article, we will delve into the basics of dividend investing, explore the benefits and risks, and provide you with practical tips on how to get started.
Understanding Dividend Investing and Its Benefits
Dividend investing is a strategy where investors buy stocks of companies that pay out a portion of their profits to shareholders in the form of dividends. These dividends are typically paid out quarterly or annually and can provide investors with a steady stream of income.
When you invest in dividend-paying stocks, you are essentially becoming a part-owner of the company. As a shareholder, you are entitled to receive a share of the company’s profits. This income can be used to supplement your existing income, reinvest in the stock market, or simply saved for future use.
Benefits of Dividend Investing
Dividend investing offers several potential benefits, including:
- Passive Income: Dividends provide a consistent stream of income, which can be helpful for investors seeking to supplement their earnings.
- Potential for Capital Appreciation: While dividends provide income, the value of the underlying stock can also appreciate over time. This means you could potentially earn both income and growth on your investment.
- Reduced Risk: Dividend-paying companies often have a track record of profitability and financial stability. This can make them less volatile than other types of investments.
- Tax Advantages: Qualified dividends are often taxed at a lower rate than other types of income, such as wages or interest income. This can provide tax savings for investors.
Factors to Consider Before Investing
Before investing in dividend stocks, it is important to consider the following factors:
- Dividend Yield: This is the annual dividend payment expressed as a percentage of the stock’s current price. A higher dividend yield generally means the company is paying out a larger portion of its profits to shareholders.
- Dividend Payout Ratio: This is the percentage of a company’s earnings that are paid out as dividends. A high payout ratio can be a sign that a company is not investing enough in growth.
- Dividend Growth History: Companies that have a history of increasing their dividends are generally considered more attractive to investors.
- Financial Strength: It is essential to invest in financially sound companies with strong earnings and a solid balance sheet.
Dividend investing can be a valuable part of a diversified investment portfolio. By carefully selecting dividend-paying stocks and understanding the factors to consider, investors can potentially generate passive income and grow their wealth over the long term.
Types of Dividend Stocks to Consider
Dividend stocks are stocks that pay out a portion of their earnings to shareholders in the form of regular cash payments, known as dividends. These stocks can be a great addition to any portfolio, as they provide a steady stream of income, which can be used for reinvestment, spending, or debt repayment. Dividend stocks can offer several advantages, including:
- Regular income: Dividends provide a consistent stream of income, which can be helpful for retirees or those seeking to supplement their income.
- Potential for capital appreciation: While not guaranteed, dividend stocks can appreciate in value over time, providing potential for capital gains.
- Reduced risk: Companies that pay dividends often have a history of profitability and stability, which can make them less risky investments.
There are many different types of dividend stocks, and the best type for you will depend on your individual investment goals and risk tolerance. Here are a few types of dividend stocks to consider:
1. High-Yield Dividend Stocks
High-yield dividend stocks are stocks that pay out a relatively high dividend yield, which is calculated by dividing the annual dividend per share by the stock’s current price. These stocks can be attractive to investors seeking a high level of income, but it is important to note that they can also be more risky.
2. Dividend Aristocrats
Dividend aristocrats are stocks that have increased their dividend payments for at least 25 consecutive years. These companies have a long history of profitability and commitment to shareholder returns, making them a more stable and reliable option for dividend income.
3. Dividend Growth Stocks
Dividend growth stocks are companies that have a track record of consistently increasing their dividend payments over time. These stocks can be a good choice for investors who want to see their dividend income grow over time. However, it is important to note that dividend growth is not guaranteed and can be affected by factors such as economic conditions and company performance.
4. Low-Volatility Dividend Stocks
Low-volatility dividend stocks are stocks that tend to experience less price fluctuation than the overall market. These stocks can be a good option for investors who are risk-averse and looking for a stable source of income.
Ultimately, the best type of dividend stock for you will depend on your specific investment goals and risk tolerance. It is important to do your research and understand the risks and potential rewards before investing in any dividend stock.
Building a Dividend Investing Strategy
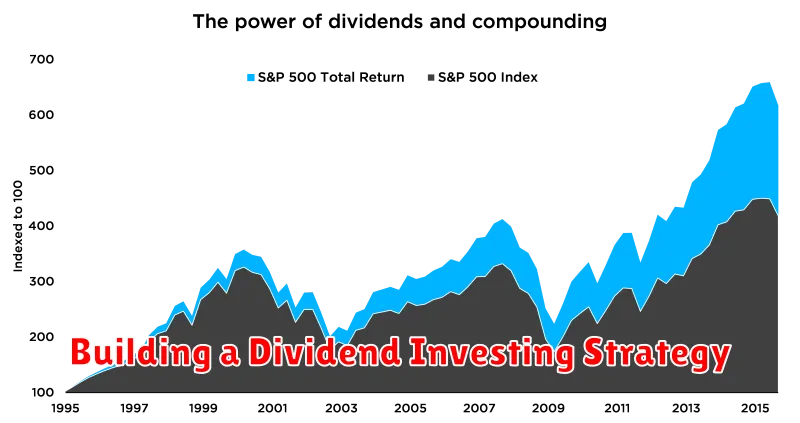
Dividend investing is a popular strategy for investors seeking to generate passive income from their portfolios. By investing in companies that pay dividends, investors can receive regular cash payments, which can be reinvested or used for other purposes. Building a successful dividend investing strategy requires careful planning and consideration of several factors.
1. Define Your Investment Goals
The first step is to define your investment goals. What are you hoping to achieve with your dividend investments? Are you looking for a steady stream of income, or are you hoping to grow your portfolio over time? Your investment goals will determine the types of companies you invest in and the amount of risk you are willing to take.
2. Determine Your Risk Tolerance
Dividend-paying companies can range from stable, mature businesses to riskier, high-growth companies. It is important to assess your risk tolerance before investing in any company. If you are risk-averse, you may want to focus on companies with a long history of paying dividends and a strong financial track record. On the other hand, if you are willing to take on more risk, you may consider investing in companies with higher dividend yields but also a higher risk of dividend cuts.
3. Research and Select Companies
Once you have defined your investment goals and determined your risk tolerance, you can begin researching and selecting companies. Look for companies with a history of paying dividends, a strong balance sheet, and a solid track record of growth. You should also consider factors such as the company’s industry, competitive landscape, and management team.
4. Diversify Your Portfolio
It is essential to diversify your dividend portfolio by investing in a range of companies across different sectors and industries. This helps to reduce risk and improve your overall return potential. It is also important to diversify your investments across different geographic locations.
5. Monitor Your Investments
Once you have built your dividend portfolio, it is important to monitor your investments regularly. Pay attention to the companies’ financial performance, dividend announcements, and any changes in the industry or economy that could affect your investments. Adjust your portfolio as needed to maintain your desired level of risk and return.
6. Reinvest Dividends
One of the best ways to grow your dividend income is to reinvest your dividends. When you reinvest your dividends, you are essentially buying more shares of the company, which increases your overall ownership and future dividend income. This process, known as dividend compounding, can significantly increase your returns over time.
7. Consider Tax Implications
Dividends are generally taxable income, and the tax rate will vary depending on your income level and the type of investment. Be sure to consider the tax implications of dividend investing before making any investment decisions.
8. Be Patient and Disciplined
Dividend investing is a long-term strategy that requires patience and discipline. Don’t expect to get rich quickly. Instead, focus on building a strong portfolio of dividend-paying companies that can provide you with a steady stream of income for many years to come.
Analyzing Dividend Stocks: Key Metrics to Look For
Dividend stocks, which distribute a portion of their profits to shareholders, can be a valuable addition to any investment portfolio. However, selecting the right dividend stocks requires careful analysis of key metrics to ensure sustainability and long-term profitability. Here are some crucial factors to consider:
Dividend Yield: This metric represents the annual dividend payment as a percentage of the stock’s current price. A higher dividend yield might seem attractive, but it’s essential to consider the company’s ability to sustain it. A low yield could signal a potentially undervalued stock or a company with lower payout ratios.
Payout Ratio: This ratio indicates the percentage of earnings a company distributes as dividends. A healthy payout ratio typically falls between 30% and 60%. A higher ratio might suggest a company is overpaying dividends, potentially impacting its future growth and financial stability.
Dividend Growth Rate: A consistent increase in dividend payments over time signals a company’s financial strength and commitment to shareholder returns. Look for companies with a history of steady dividend growth, even during economic downturns.
Debt-to-Equity Ratio: A high debt-to-equity ratio signifies a company’s heavy reliance on borrowing, which could negatively impact its ability to sustain dividends. A lower ratio indicates a healthier financial position.
Return on Equity (ROE): This metric measures a company’s profitability in relation to its shareholder equity. A higher ROE generally signifies a more efficient company that can generate higher returns for shareholders, including dividends.
Free Cash Flow (FCF): Free cash flow represents the cash a company has left over after paying for operating expenses and capital investments. A strong FCF enables companies to fund dividends and reinvest in growth.
Dividend Coverage Ratio: This ratio measures a company’s ability to cover its dividend payments with its earnings. A ratio greater than one indicates that the company can easily cover its dividend payments, while a ratio less than one suggests a potential risk of dividend cuts.
Industry Trends: It’s important to analyze the overall industry trends and the company’s competitive position within that industry. Factors like regulatory changes, technological advancements, and consumer demand can influence a company’s ability to maintain its dividend payments.
Company Management: Understanding the company’s management team, their track record, and their commitment to shareholder value is crucial. A strong and experienced leadership team can significantly impact a company’s dividend sustainability.
By carefully analyzing these metrics and considering the overall financial health of the company, investors can identify dividend stocks with a high probability of success. Remember, while dividends can provide a steady stream of income, it’s essential to diversify your portfolio and invest for the long term to mitigate risk and maximize potential returns.
Finding and Researching Dividend-Paying Companies

Investing in dividend-paying companies can be a great way to generate passive income and grow your portfolio over time. However, it’s important to do your research and choose companies that are financially sound and have a history of consistent dividend payments. Here’s a guide on how to find and research dividend-paying companies:
1. Start with Online Brokerage Platforms
Most online brokerage platforms allow you to filter stocks by their dividend yield. You can also set other criteria, such as market capitalization, sector, and industry. This makes it easy to narrow down your search and find companies that fit your investment goals.
2. Utilize Financial Websites and Databases
Websites like Yahoo Finance, Google Finance, and Morningstar offer comprehensive financial information about publicly traded companies, including their dividend history, payout ratio, and dividend growth rate. You can also use databases like S&P Global Market Intelligence to access in-depth financial data.
3. Look for Companies with a Strong Track Record
When researching dividend-paying companies, it’s crucial to look for those with a history of consistent dividend payments. A long-term dividend track record suggests that the company is financially stable and committed to rewarding shareholders. Consider factors such as dividend growth, payout ratio, and dividend coverage ratio.
4. Analyze the Company’s Financial Health
Examine the company’s financial statements, including its balance sheet, income statement, and cash flow statement. Look for signs of financial stability, such as strong revenue growth, healthy profit margins, and adequate cash flow. It’s also important to assess the company’s debt levels and leverage.
5. Consider Industry Trends and Competition
Understanding the industry in which the company operates is essential. Analyze industry growth prospects, competition, and technological advancements. A strong industry outlook and competitive advantage can contribute to the company’s long-term dividend sustainability.
6. Pay Attention to Management and Corporate Governance
Investigate the company’s management team and corporate governance practices. Look for experienced leaders with a proven track record and a commitment to shareholder value. Strong corporate governance ensures transparency, accountability, and responsible decision-making.
7. Stay Informed and Monitor Your Investments
Regularly monitor your investments and stay updated on company news, industry trends, and economic conditions. This will help you make informed decisions about your portfolio and ensure that your dividend-paying companies are still meeting your expectations.
Finding and researching dividend-paying companies requires careful consideration and due diligence. By following these steps, you can increase your chances of investing in financially sound companies that offer the potential for long-term dividend growth and passive income.
Managing Your Dividend Portfolio for Long-Term Growth
Dividend investing is a popular strategy for long-term growth. By investing in companies that pay dividends, you can generate passive income and potentially increase your portfolio’s value over time. However, managing a dividend portfolio requires careful planning and execution.
Here are some key strategies for managing your dividend portfolio for long-term growth:
1. Diversify Your Portfolio
Diversification is essential for mitigating risk and maximizing returns. It’s vital to spread your investments across different sectors, industries, and geographies. This approach helps you avoid overexposure to any particular company or industry, making your portfolio more resilient in the face of market fluctuations.
2. Focus on Quality Companies
Investing in companies with a strong track record of profitability and dividend growth is essential. Look for businesses with robust financial positions, competitive advantages, and a history of consistent dividend payments. By selecting high-quality companies, you can build a portfolio that is well-positioned for long-term growth.
3. Consider Dividend Growth
Dividend growth is a key factor to consider when selecting dividend-paying stocks. Companies that consistently increase their dividends are typically growing their businesses and generating strong profits. Aim to build a portfolio of companies with a history of increasing dividends, which can provide a steady stream of income and potential for capital appreciation.
4. Monitor Your Portfolio Regularly
Regular monitoring is crucial for managing any investment portfolio, and dividend portfolios are no exception. Keep track of your investments, monitor company performance, and review your asset allocation. Periodically assess the dividend-paying abilities of your holdings and consider adjusting your portfolio based on your investment goals and market conditions.
5. Reinvest Your Dividends
Dividend reinvestment is a powerful tool for compounding growth. By automatically reinvesting your dividends back into your portfolio, you can buy more shares of the companies you own, increasing your overall exposure and potential for future growth. This strategy can contribute significantly to the long-term growth of your dividend portfolio.
6. Be Patient and Disciplined
Dividend investing is a long-term strategy, and success requires patience and discipline. Avoid reacting to short-term market fluctuations and stick to your investment plan. Remain committed to your long-term goals, and resist the urge to sell your shares during market downturns. Over time, the power of compounding and consistent dividend income can lead to substantial portfolio growth.
By following these strategies, you can create a dividend portfolio that provides a steady stream of income, potentially increases in value over time, and helps you reach your financial goals.
Dividend Reinvestment: Accelerating Your Wealth Building
Dividend reinvestment, also known as DRIP, is a powerful strategy for long-term investors looking to accelerate their wealth building. It’s a simple yet effective way to harness the power of compounding returns. With a DRIP plan, you automatically reinvest your dividend payments into additional shares of the same company, effectively buying more stock without having to lift a finger.
One of the key advantages of DRIP is that it eliminates the need for you to manually buy more shares. You don’t have to monitor stock prices, pay brokerage fees, or worry about the timing of your purchases. It all happens automatically, allowing you to focus on other aspects of your financial life.
DRIP also helps you benefit from compounding. Each time your dividends are reinvested, you acquire more shares, which in turn generate more dividends. This snowball effect leads to exponential growth over time, as you gain more and more shares without actively buying them. Think of it like planting a seed that grows into a tree and produces more seeds that grow into more trees, and so on.
Furthermore, DRIP offers a way to dollar-cost average your investment. By regularly investing a small amount, you avoid the risk of buying a stock at a high price point. The strategy allows you to buy more shares when prices are low and fewer shares when prices are high, smoothing out the impact of market fluctuations.
However, it’s crucial to remember that DRIP isn’t a get-rich-quick scheme. While it can significantly enhance your returns, it’s important to understand that dividends are not guaranteed. The amount you receive can vary depending on the company’s performance and its dividend policy.
If you’re considering a DRIP strategy, research the specific company and its dividend history. Assess its financial health, track its track record of dividend payouts, and understand the potential risks involved. It’s also a good idea to consult with a financial advisor to determine if a DRIP plan aligns with your overall investment goals.
In conclusion, dividend reinvestment can be a valuable tool for long-term investors looking to build wealth. It’s a simple yet powerful strategy that can help you harness the power of compounding returns and potentially accelerate your financial growth. By automating your reinvestments, you can benefit from the magic of compounding and steadily grow your portfolio, one dividend at a time.
Tax Implications of Dividend Income
Dividends are payments made by companies to their shareholders, usually in the form of cash, stock, or other assets. Dividends are considered taxable income and are subject to different tax rates depending on the type of dividend and the investor’s tax bracket.
There are two main types of dividends: qualified dividends and non-qualified dividends.
Qualified Dividends
Qualified dividends are typically paid by U.S. corporations and meet certain holding period requirements. They are taxed at a lower rate than ordinary income, often at the same rate as long-term capital gains. The current tax rates for qualified dividends are:
- 10% for those in the 10% or 12% tax brackets
- 15% for those in the 22%, 24%, 32%, or 35% tax brackets
- 20% for those in the 37% tax bracket
Non-Qualified Dividends
Non-qualified dividends are typically paid by foreign corporations or do not meet the holding period requirements for qualified dividends. They are taxed at the investor’s ordinary income tax rate, which can be significantly higher than the qualified dividend tax rate.
Tax Reporting
Dividends received are typically reported on Form 1099-DIV. The form lists the amount of dividends received, including the amount of qualified and non-qualified dividends. Investors should carefully review their Form 1099-DIV and consult with a tax professional to ensure they are correctly reporting their dividend income.
Dividend Reinvestment
Many investors choose to reinvest their dividends back into the company’s stock. This strategy can help investors grow their investment over time, but it is important to note that dividend reinvestment plans often have tax implications. While you are not taxed on the dividend payment immediately, you will be taxed on the growth of your investment when you eventually sell your shares.
Tax Planning
It is important to consider the tax implications of dividend income when making investment decisions. Investors may be able to reduce their tax liability by strategically investing in tax-advantaged accounts such as Roth IRAs or 401(k) plans. Consulting with a tax professional can help investors develop a tax plan that minimizes their tax burden.

