Are you a self-employed individual looking to secure your financial future? Retirement planning may seem daunting, but it’s crucial for your long-term well-being. As a self-employed worker, you have the flexibility to choose your own retirement savings strategies, but that freedom can also come with challenges. Navigating the complex world of retirement planning can be overwhelming, but don’t worry! This guide will equip you with the knowledge and tools needed to create a solid retirement plan.
This article will delve into key retirement savings strategies specifically designed for the self-employed, exploring the benefits and nuances of each option. Whether you’re just starting your self-employment journey or are looking to optimize your current plan, this guide will provide valuable insights. We’ll uncover how to maximize your contributions, understand tax advantages, and make informed decisions that align with your financial goals. Get ready to learn how to secure a comfortable retirement while enjoying the freedom of self-employment!
Understanding the Importance of Retirement Savings as a Self-Employed Individual
Being self-employed offers numerous perks, including flexibility and independence. However, it also comes with responsibilities, one of which is planning for retirement. While traditional employees enjoy employer-sponsored retirement plans, self-employed individuals must proactively take charge of their financial future.
Retirement savings are crucial for self-employed individuals for several reasons:
- Financial Security: Securing a comfortable retirement is essential, especially when you are solely responsible for your income. Retirement savings provide a safety net to cover living expenses, healthcare costs, and leisure activities.
- Tax Advantages: Self-employed individuals can benefit from tax advantages associated with retirement plans like solo 401(k)s and SEP IRAs. These plans allow for pre-tax contributions, reducing your current tax liability and growing your savings tax-deferred.
- Long-Term Growth: Retirement savings offer a long-term investment opportunity. With time, your contributions can grow through compounding, helping you accumulate a substantial nest egg for the future.
- Peace of Mind: Knowing you are financially prepared for retirement can provide immense peace of mind, allowing you to enjoy your golden years without worrying about financial burdens.
Here are some tips for self-employed individuals to maximize their retirement savings:
- Establish a Retirement Plan: Choose a suitable retirement plan, such as a solo 401(k) or SEP IRA, and start contributing regularly.
- Set Savings Goals: Determine your desired retirement income and establish realistic savings goals to reach that target.
- Contribute Consistently: Make regular contributions to your retirement plan, even if it’s just a small amount. Consistency is key to long-term growth.
- Seek Professional Advice: Consult with a financial advisor to create a comprehensive retirement plan tailored to your individual needs and circumstances.
Retirement planning is an important aspect of self-employment. By prioritizing retirement savings, you can secure a financially stable future and enjoy a fulfilling retirement.
Exploring Different Retirement Savings Plans for the Self-Employed
Being self-employed offers a great deal of flexibility and control over your work life, but it also comes with the added responsibility of managing your own retirement savings. Unlike employees who have access to employer-sponsored retirement plans like 401(k)s, the self-employed need to actively seek out retirement savings options that suit their needs and goals.
Fortunately, there are several retirement savings plans specifically designed for the self-employed, offering various advantages and tax benefits. Understanding the different options available can help you make informed decisions and secure your financial future.
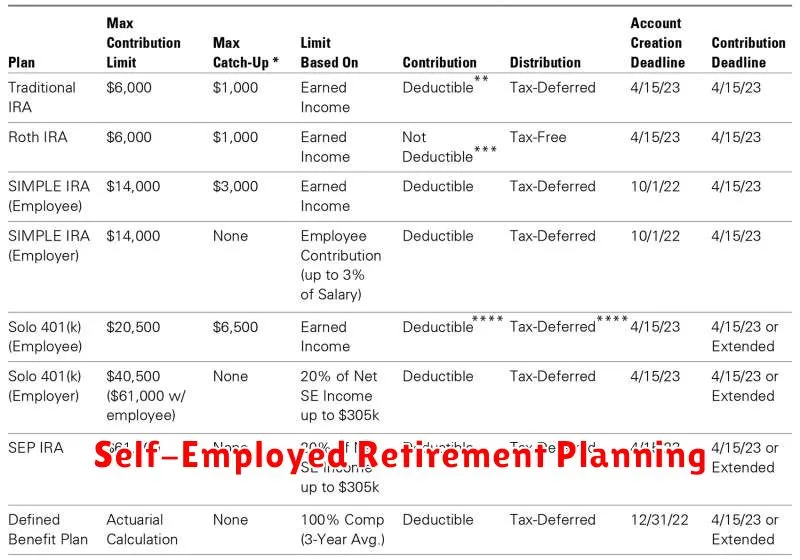
1. Solo 401(k)
A Solo 401(k) is a retirement savings plan designed for self-employed individuals and small business owners with no employees or only a spouse working in the business. This plan allows you to contribute both as an employee and an employer, offering greater flexibility in contributions and potential tax advantages.
Key Features:
- You can contribute both as an employee and an employer.
- You can choose between a traditional or Roth Solo 401(k) plan.
- Higher contribution limits compared to traditional IRAs.
- Tax-deferred growth and tax-free withdrawals in retirement.
2. SEP IRA
A Simplified Employee Pension (SEP) IRA is a retirement savings plan that allows self-employed individuals and small business owners to make contributions on their own behalf. It offers a straightforward and easy-to-administer option for those who prefer a simple retirement savings solution.
Key Features:
- Contributions are made directly to a traditional IRA.
- You can contribute up to 25% of your net adjusted self-employed income.
- Contributions are tax-deductible, reducing your current tax liability.
- Withdrawals in retirement are taxed as ordinary income.
3. Keogh Plan (Defined Contribution Plan)
A Keogh plan, also known as a defined contribution plan, is a retirement savings plan available to self-employed individuals and small business owners. It provides flexibility in contribution strategies and asset allocation, allowing you to customize your retirement savings approach.
Key Features:
- You can choose between a traditional or Roth Keogh plan.
- Higher contribution limits than traditional IRAs.
- Tax-deferred growth and tax-free withdrawals in retirement for traditional Keogh plans.
4. SIMPLE IRA
A Savings Incentive Match Plan for Employees (SIMPLE) IRA is a retirement plan designed for small businesses with 100 or fewer employees. It provides a relatively simple and affordable option for employers to offer retirement savings benefits.
Key Features:
- Contributions are made directly to a traditional IRA.
- You can contribute up to $15,500 in 2023, plus an additional $3,500 if you are age 50 or older.
- Tax-deferred growth and tax-free withdrawals in retirement.
Choosing the Right Retirement Savings Plan
The best retirement savings plan for you will depend on your individual circumstances, financial goals, and risk tolerance. It’s essential to consider factors such as your income, expenses, desired retirement income, and time horizon.
It’s highly recommended to consult with a qualified financial advisor to discuss your specific situation and determine the most appropriate retirement savings plan for your needs. They can help you analyze your financial situation, understand the tax implications, and make informed decisions about your retirement savings strategy.
Solo 401(k): A Powerful Option for Self-Employed Individuals and Small Business Owners

If you’re self-employed or own a small business, you’re likely aware of the importance of saving for retirement. But you might be overwhelmed by the various options available to you. One powerful tool you can utilize is a Solo 401(k), a retirement savings plan designed specifically for self-employed individuals and small business owners.
What is a Solo 401(k)?
A Solo 401(k), also known as an individual 401(k), allows you to contribute as both an employee and an employer. This means you can make contributions in two different capacities, maximizing your retirement savings potential.
Benefits of a Solo 401(k)
Here are some key benefits of a Solo 401(k):
- Tax Advantages: Contributions to a Solo 401(k) are tax-deductible, allowing you to reduce your current tax liability. Additionally, earnings on your contributions grow tax-deferred, meaning you won’t be taxed on them until you withdraw the funds in retirement.
- High Contribution Limits: Solo 401(k)s have much higher contribution limits than traditional IRAs. This allows you to save a significant amount for retirement, especially if you have a high income.
- Flexibility: You have control over your investment options within a Solo 401(k). You can choose from a variety of investments, including stocks, bonds, mutual funds, and real estate.
- Simplicity: Setting up and managing a Solo 401(k) is generally simpler than other retirement plans, as you are both the employee and the employer.
Eligibility Requirements
To be eligible for a Solo 401(k), you must meet the following requirements:
- Be self-employed or own a small business.
- Have no employees other than yourself or your spouse.
- Be at least 18 years old.
Contribution Limits
For 2023, the total annual contribution limit for a Solo 401(k) is $66,000, or $73,500 if you are 50 or older. This limit is divided into two parts:
- Employee Contribution: You can contribute up to $22,500 (or $30,000 if you are 50 or older) as an employee.
- Employer Contribution: You can contribute up to 25% of your net adjusted self-employed income.
Withdrawal Rules
Withdrawals before age 59 1/2 are generally subject to a 10% penalty, as well as your usual tax rate. However, you can withdraw your contributions (not earnings) at any time without penalty. You can also withdraw funds for certain hardship situations, such as medical expenses or the purchase of a home.
Conclusion
A Solo 401(k) can be a powerful retirement savings tool for self-employed individuals and small business owners. It offers significant tax advantages, high contribution limits, and flexibility. If you’re looking for a way to secure your financial future, a Solo 401(k) is definitely worth considering.
SEP IRA: Simplified Retirement Savings for Small Business Owners

Are you a small business owner looking for a simple and effective way to save for retirement? A SEP IRA (Simplified Employee Pension IRA) might be the perfect solution for you.
A SEP IRA is a retirement plan that allows self-employed individuals and small business owners to make contributions on their own behalf and, if they choose, on behalf of their employees. This type of IRA is incredibly flexible and straightforward, making it a popular choice for small business owners who want to maximize their retirement savings.
Key Benefits of a SEP IRA:
- Simplicity: SEP IRAs are relatively easy to set up and manage. There’s no need for complex paperwork or ongoing administrative tasks.
- Flexibility: You have the flexibility to choose the amount you contribute each year, up to a certain limit. This allows you to adjust your contributions based on your income and financial situation.
- Tax Advantages: Contributions to a SEP IRA are tax-deductible, meaning you can reduce your taxable income and potentially save on taxes.
- Tax-Deferred Growth: Your earnings and investments in a SEP IRA grow tax-deferred, meaning you won’t pay taxes on them until you withdraw them in retirement.
Who Can Benefit from a SEP IRA?
A SEP IRA can be a great option for a variety of small business owners, including:
- Sole proprietorships
- Partnerships
- Corporations (S-corps and C-corps)
How to Set Up a SEP IRA:
To open a SEP IRA, you’ll need to contact a financial institution that offers these accounts. The process is typically straightforward, and you’ll need to provide some basic information about your business and your employees.
Contribution Limits:
The maximum contribution amount for a SEP IRA is 25% of your net adjusted self-employed income, up to a maximum of $66,000 for 2023. This means that if your adjusted self-employed income is $100,000, you can contribute up to $25,000 to your SEP IRA.
Withdrawal Rules:
You can typically withdraw money from a SEP IRA without penalty at age 59 1/2. Withdrawals before age 59 1/2 may be subject to a 10% penalty, as well as your usual income tax rate. However, certain exceptions exist, such as for certain disabilities or death.
Conclusion:
A SEP IRA can be a powerful tool for small business owners looking to save for retirement. Its simplicity, flexibility, and tax benefits make it an attractive option for those who want to maximize their savings and secure a comfortable future. If you’re a small business owner considering a retirement plan, a SEP IRA is definitely worth exploring.
SIMPLE IRA: A Straightforward Option for Small Businesses
If you’re a small business owner, you know that providing retirement benefits to your employees can be a challenge. You may not have the resources or expertise to manage a complex 401(k) plan, and you want to keep things simple. That’s where a SIMPLE IRA comes in.
A SIMPLE IRA (Savings Incentive Match Plan for Employees) is a retirement savings plan that’s designed specifically for small businesses. It’s a relatively straightforward plan to set up and administer, and it offers a variety of tax advantages for both employers and employees.
Benefits of a SIMPLE IRA
Here are some of the key benefits of a SIMPLE IRA:
- Easy to Set Up and Administer: SIMPLE IRAs are much simpler to set up and administer than traditional 401(k) plans. The IRS provides a lot of flexibility in how you can structure a SIMPLE IRA, and there are no complex vesting schedules or complicated regulations to navigate.
- Tax Advantages: Contributions to a SIMPLE IRA are tax-deferred, meaning you don’t have to pay taxes on the money until you withdraw it in retirement. Additionally, both employers and employees can make tax-deductible contributions.
- Employee Participation: All eligible employees must be offered the opportunity to participate in a SIMPLE IRA.
- Employer Matching Contributions: Employers are required to make matching contributions to their employees’ SIMPLE IRAs, which can help incentivize employees to save for retirement.
Who Is a SIMPLE IRA Right For?
A SIMPLE IRA can be a good option for small businesses with:
- Fewer than 100 Employees: The SIMPLE IRA is designed for small businesses and is limited to businesses with 100 or fewer employees.
- Limited Administrative Resources: SIMPLE IRAs are relatively simple to set up and administer, making them a good option for businesses that don’t have a lot of administrative resources.
- Desire for Simplicity: If you want a retirement plan that’s easy to understand and manage, a SIMPLE IRA may be the right choice for you.
Understanding SIMPLE IRA Contribution Limits
There are limits on how much you can contribute to a SIMPLE IRA each year. For 2023, the maximum contribution amount is $15,500 for individuals and $22,500 for those aged 50 and over. Employers are required to match employee contributions up to 2% of their salary or 3% of their salary, whichever is less. If your employees choose to contribute, the employer must match.
Key Considerations
While SIMPLE IRAs offer several advantages, they also have some drawbacks to consider:
- Lower Contribution Limits: The maximum annual contribution to a SIMPLE IRA is lower than the contribution limit for traditional 401(k) plans.
- Limited Investment Options: You may have fewer investment options available to you in a SIMPLE IRA compared to a traditional 401(k) plan.
- Potential for Penalties: Early withdrawals from a SIMPLE IRA may be subject to penalties.
Conclusion
If you’re a small business owner looking for a straightforward and affordable retirement plan for your employees, a SIMPLE IRA is an excellent option to consider. By providing this valuable benefit to your employees, you can attract and retain top talent while also promoting financial security for your team.
Defining Your Retirement Goals and Risk Tolerance
Retirement planning is a crucial aspect of financial well-being, and it starts with defining your retirement goals and understanding your risk tolerance. These two factors are interconnected and will guide your investment strategy and financial decisions throughout your journey toward retirement.
Retirement Goals
Your retirement goals are what you aspire to achieve during your post-working years. These goals can be both financial and non-financial. Some common financial goals include:
- Maintaining your current lifestyle: This involves having enough income to cover your daily expenses, travel, and hobbies.
- Paying off debt: You might aim to be debt-free by retirement, which could include mortgage payments, credit card debt, or other loans.
- Leaving an inheritance: You might want to leave a financial legacy for your loved ones.
- Funding specific projects: You might have dreams of travel, home renovations, or starting a business in retirement.
Non-financial goals could include:
- Spending more time with family and friends
- Pursuing hobbies and passions
- Giving back to your community
Risk Tolerance
Your risk tolerance measures how comfortable you are with the possibility of losing money in your investments. It’s influenced by factors such as:
- Your age and time horizon: Younger investors with a longer time horizon can generally tolerate more risk.
- Your financial situation: Your current income, savings, and debt levels play a role.
- Your personality: Some people are naturally more risk-averse than others.
Here’s a simplified way to think about risk tolerance:
- High risk tolerance: You’re comfortable with the possibility of significant losses, seeking potentially higher returns.
- Moderate risk tolerance: You balance potential gains with the need for stability and security.
- Low risk tolerance: You prioritize safety and prefer investments with minimal risk, even if it means lower returns.
Connecting Goals and Risk Tolerance
Once you’ve defined your retirement goals and understood your risk tolerance, you can start to align your investment strategy. Here’s a general approach:
- Aggressive goals with high risk tolerance: You might consider a portfolio with a higher allocation to stocks, which have the potential for higher returns but also greater volatility.
- Conservative goals with low risk tolerance: You might prefer a portfolio with a greater proportion of bonds and cash, which offer more stability but potentially lower returns.
It’s essential to consult with a financial advisor to create a personalized retirement plan that aligns with your specific circumstances, goals, and risk tolerance. They can help you develop a diversified investment portfolio that balances risk and reward to help you reach your retirement aspirations.
Determining Your Retirement Savings Contributions
Retirement savings can seem like a daunting task, but with the right strategy, you can set yourself up for a comfortable future. A crucial step in planning your retirement is determining how much to contribute to your savings each month. Here’s a breakdown of factors to consider:
1. Your Retirement Goals
The first step is to define what your retirement looks like. How long do you want to retire? What lifestyle do you envision? Do you have any specific goals, like traveling or buying a second home? Once you have a clear vision, you can estimate the amount of money you’ll need to achieve it. Use online retirement calculators or consult with a financial advisor to get personalized estimates.
2. Your Current Savings
Take stock of your existing savings. Assess your 401(k) balances, IRAs, and any other retirement accounts. This will give you a starting point and help you understand how much more you need to save.
3. Your Time Horizon
The number of years you have until retirement plays a significant role in your contributions. The longer you have to invest, the more time your money has to grow. A shorter timeframe might require higher contributions to reach your goals.
4. Your Income and Expenses
Calculate your current income and expenses, including housing, food, transportation, and debt payments. This will help you determine how much you can realistically save each month. A good starting point is to aim for 10-15% of your gross income, but adjust this based on your specific circumstances.
5. Your Employer Match
If your employer offers a 401(k) match, take full advantage of it! It’s essentially free money, so maximizing your contributions to receive the full match is a wise strategy.
6. Your Risk Tolerance
How comfortable are you with market fluctuations? Your investment strategy will depend on your risk tolerance. If you’re risk-averse, you might favor lower-risk investments like bonds. If you’re comfortable with higher risk, you might consider a greater allocation to stocks.
7. Your Age
Your age plays a role in your contributions. Younger individuals generally have more time for their investments to grow, allowing them to take on more risk. As you approach retirement, you may want to shift your focus to less risky investments to preserve your capital.
8. Inflation
Inflation can erode the purchasing power of your savings over time. Consider factoring in an estimated inflation rate when calculating your contributions. A higher inflation rate might require you to save more to maintain your desired standard of living in retirement.
9. Your Health and Life Expectancy
Your health and life expectancy can impact your retirement savings needs. If you anticipate living longer than average or having significant healthcare expenses, you may need to save more.
10. Your Financial Situation
Take into account any other financial obligations you may have, such as student loans or mortgages. Your retirement savings contributions should be adjusted to fit within your overall financial plan.
11. Consider Professional Advice
If you’re unsure about your retirement savings strategy, consult with a financial advisor. They can provide personalized guidance based on your unique circumstances and help you create a plan to achieve your goals.
12. Adjust as Needed
Your retirement savings plan should be a living document. Review it regularly and adjust your contributions as your income, expenses, and goals change. Be proactive and make necessary adjustments to ensure you’re on track for a successful retirement.
Retirement planning involves many factors, and determining your savings contributions is an essential step. By considering these factors and taking a proactive approach, you can set yourself up for a comfortable and financially secure future.
Investment Strategies for Self-Employed Retirement Plans
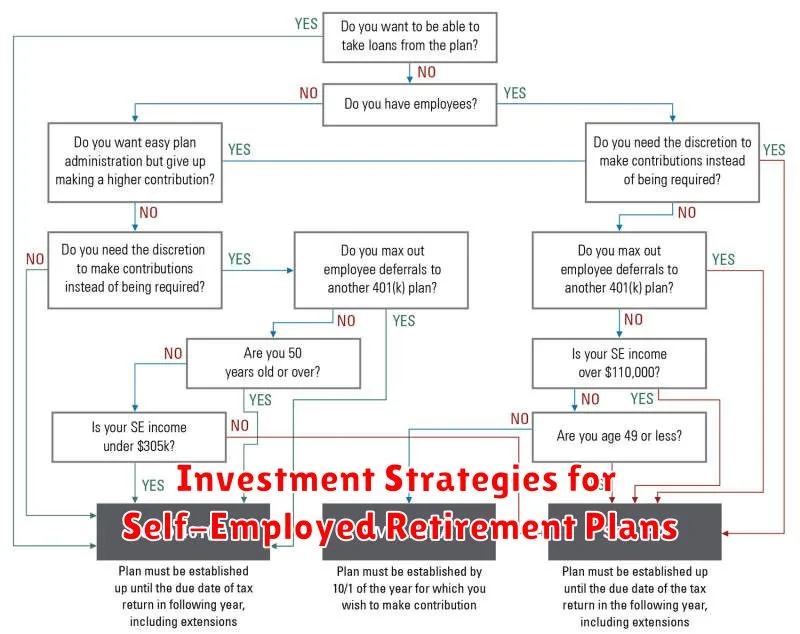
As a self-employed individual, you have the freedom to set your own hours, choose your projects, and build a business that aligns with your passions. But this freedom comes with a significant responsibility: planning for your retirement. Unlike traditional employees who benefit from employer-sponsored retirement plans, you must take the initiative to secure your financial future.
One of the most effective ways to save for retirement as a self-employed individual is through a self-employed retirement plan. These plans offer several advantages, including tax benefits, flexibility, and control over your investment decisions.
Here are some investment strategies to consider for your self-employed retirement plan:
1. Diversify Your Portfolio
Diversification is a fundamental principle of investing that aims to reduce risk by spreading your investments across different asset classes. This includes stocks, bonds, real estate, and commodities. A well-diversified portfolio can help you weather market fluctuations and achieve long-term growth.
2. Consider a Target-Date Fund
Target-date funds are a convenient and low-maintenance option for self-employed individuals. These funds automatically adjust their asset allocation over time, becoming more conservative as you approach retirement. This strategy helps mitigate risk and ensures your investments are aligned with your age and time horizon.
3. Explore Alternative Investments
While traditional investments like stocks and bonds are essential, don’t be afraid to explore alternative investments. These could include private equity, venture capital, or even precious metals. These investments can offer higher potential returns but often come with greater risks. It’s essential to conduct thorough research and consult with a financial advisor before making any significant allocation.
4. Regularly Review and Adjust Your Investments
Your financial needs and goals will evolve throughout your career. As your circumstances change, it’s crucial to review your retirement portfolio and make adjustments as needed. Consider factors like your risk tolerance, time horizon, and investment performance. Rebalancing your portfolio ensures that your investments align with your current goals and objectives.
5. Seek Professional Advice
Navigating the complexities of self-employed retirement planning can be challenging. Consider seeking professional advice from a qualified financial advisor. A financial advisor can help you develop a personalized investment strategy, manage your investments, and provide ongoing guidance throughout your retirement journey.
Planning for retirement is an essential aspect of being self-employed. By implementing these investment strategies, you can build a solid foundation for your financial security and enjoy the fruits of your hard work in your golden years.
Maximizing Tax Benefits and Deductions
Navigating the complex world of taxes can be daunting, but understanding the various tax benefits and deductions available to you can significantly reduce your tax liability. By taking advantage of these opportunities, you can keep more of your hard-earned money in your pocket. This article will delve into key strategies for maximizing your tax benefits and deductions, empowering you to make informed financial decisions.
Understanding Your Filing Status
Your filing status plays a crucial role in determining your tax obligations. It influences the tax brackets you fall into, standard deductions, and other tax-related benefits. The most common filing statuses include:
- Single: For individuals who are unmarried or legally separated.
- Married Filing Jointly: For married couples who choose to combine their incomes and file jointly.
- Married Filing Separately: For married couples who prefer to file their taxes separately.
- Head of Household: For unmarried individuals who pay more than half of the costs of maintaining a home for a qualifying child or dependent.
- Qualifying Widow(er) with Dependent Child: For surviving spouses who meet certain criteria, such as having a dependent child living with them.
It’s essential to choose the filing status that best reflects your personal circumstances to maximize your tax benefits.
Standard Deduction vs. Itemized Deductions
When filing your taxes, you have the option of claiming either the standard deduction or itemizing your deductions. The standard deduction is a fixed amount that varies based on your filing status, while itemized deductions allow you to deduct specific expenses.
To determine which option is most beneficial, compare the total value of your itemized deductions to the standard deduction for your filing status. If your itemized deductions exceed the standard deduction, itemizing is likely to result in a lower tax liability. However, if the standard deduction is higher, claiming it will save you more on your taxes.
Common Tax Deductions
There are numerous tax deductions available to individuals and families, depending on their income, expenses, and other factors. Here are some of the most common tax deductions:
- Homeownership: Mortgage interest, property taxes, and insurance premiums can be deducted.
- Medical Expenses: Deductible medical expenses exceeding a certain percentage of your adjusted gross income.
- Charitable Contributions: Donations to qualified charities can be deducted.
- State and Local Taxes (SALT): Deductions for state and local income taxes and property taxes, subject to limitations.
- Child Tax Credit: A tax credit for each qualifying child under the age of 17.
- Education Expenses: Deductions for tuition and other educational expenses.
- Business Expenses: Deductible expenses related to self-employment or small businesses.
Remember to keep accurate records of all your expenses and consult with a tax professional to ensure you’re taking advantage of all eligible deductions.
Tax Credits vs. Deductions
Tax credits and deductions are both ways to reduce your tax liability, but they work differently. While deductions reduce your taxable income, tax credits directly reduce your tax liability.
For example, if you claim a $1,000 deduction, your taxable income is reduced by $1,000, resulting in a lower tax bill. However, if you claim a $1,000 tax credit, your tax liability is directly reduced by $1,000, regardless of your income level. Tax credits are often considered more valuable than deductions as they provide a dollar-for-dollar reduction in your tax burden.
Seeking Professional Advice
Navigating the complex tax code can be overwhelming. Consulting with a qualified tax professional can provide invaluable guidance and ensure you’re maximizing your tax benefits and deductions. A tax advisor can help you understand your filing status, identify all eligible deductions and credits, and optimize your tax strategies for the current tax year.