Investing is one of the most important things you can do to secure your financial future. But, with all the different investment options and fees involved, it can be hard to know where to start. One of the most important things to consider when investing is investment fees. These fees can eat away at your returns, making it harder for you to grow your wealth. Luckily, there are several things you can do to minimize investment fees and get the most out of your investments.
In this article, we will discuss how to minimize investment fees. We’ll cover different types of fees, provide tips on choosing low-cost investments, and explore strategies for reducing hidden fees. By following these tips, you can save money on investment fees and potentially increase your returns. Whether you’re just starting out or an experienced investor, understanding and managing investment fees is essential to building a solid financial foundation.
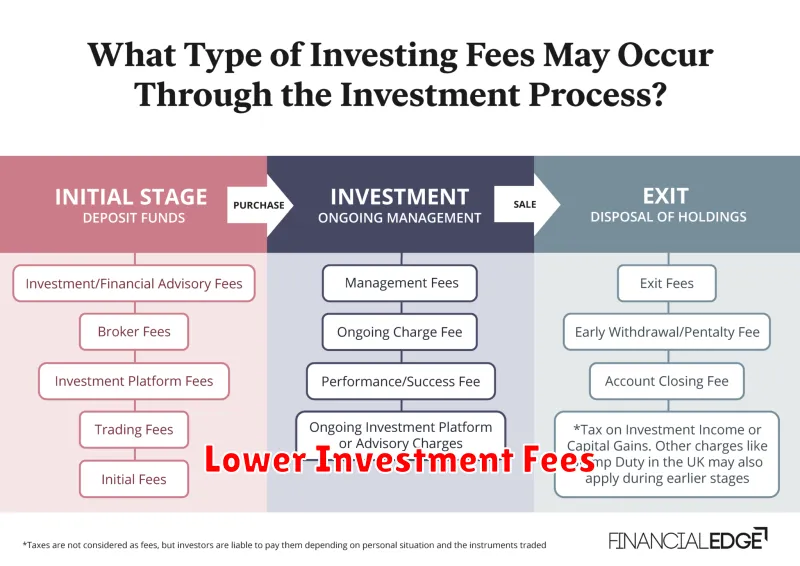
Understanding Different Types of Investment Fees
Investing can be a great way to grow your wealth over time, but it’s important to understand the different types of fees you may encounter along the way. These fees can eat into your returns, so it’s crucial to choose investments that are transparent and cost-effective.
Types of Investment Fees
Here are some of the most common types of investment fees:
- Advisory Fees: These are charged by financial advisors for providing investment advice and managing your portfolio. They can be charged as a percentage of assets under management (AUM) or as a flat fee.
- Trading Commissions: These are fees charged when you buy or sell securities. They can vary depending on the brokerage firm and the type of security you’re trading.
- Management Fees: These are charged by mutual funds and exchange-traded funds (ETFs) to cover the costs of managing the fund’s portfolio. They are typically expressed as an annual percentage of your investment.
- Expense Ratios: This is an annual fee that covers the costs of running a mutual fund or ETF. It includes things like management fees, administrative costs, and marketing expenses. Expense ratios are expressed as a percentage of the fund’s assets.
- Load Fees: These are one-time fees charged when you buy or sell shares of a mutual fund. Load fees can be front-end, back-end, or contingent.
How to Avoid High Fees
Here are some tips for avoiding high investment fees:
- Choose low-cost investments: Look for funds with low expense ratios and avoid funds with high load fees.
- Negotiate with advisors: Don’t be afraid to negotiate advisory fees with financial advisors, especially if you have a large portfolio.
- Consider robo-advisors: Robo-advisors offer automated investment services at lower fees than traditional financial advisors.
- Do your research: Compare fees and expense ratios across different investments before making a decision.
Understanding investment fees is crucial for maximizing your returns. By carefully considering the fees you pay, you can make sure your investments are working for you, not against you.
The Impact of Fees on Investment Returns
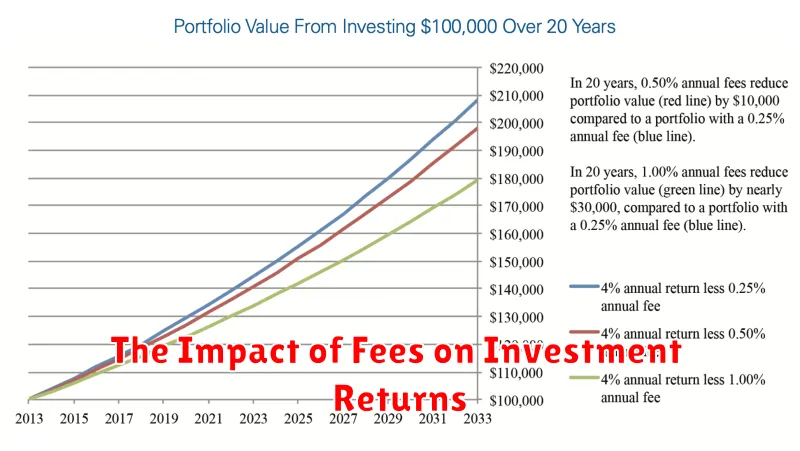
Fees are an unavoidable part of investing, but they can have a significant impact on your returns over time. Understanding the different types of fees and how they can affect your investment performance is crucial for maximizing your returns.
Expense Ratios: This is a percentage of your assets that is charged annually to cover the costs of managing your investment. While it may seem small, it can significantly reduce your returns over the long term. For example, an expense ratio of 1% may seem insignificant, but over 20 years, it can reduce your total return by nearly 20%!
Trading Commissions: These fees are charged when you buy or sell securities. While online brokers have made these fees much lower, they can still add up over time, especially if you trade frequently.
Advisory Fees: If you use a financial advisor, they will typically charge a fee for their services. This fee can be based on a percentage of your assets, a flat fee, or an hourly rate.
Load Fees: These fees are charged when you buy or sell mutual funds. Front-end loads are charged when you buy the fund, while back-end loads are charged when you sell it. Load fees can be substantial, so it’s important to consider them carefully when choosing a mutual fund.
The Impact of Fees on Returns: Even small fees can significantly impact your investment returns over time. As we mentioned before, a 1% expense ratio can reduce your returns by nearly 20% over 20 years! This is why it’s crucial to invest in low-cost funds and minimize trading commissions whenever possible.
How to Minimize Fees: Here are some tips for minimizing fees on your investments:
- Invest in low-cost index funds: Index funds track a specific market index, such as the S&P 500. They have lower expense ratios than actively managed funds because they don’t require as much research and trading.
- Use a discount broker: Discount brokers offer lower trading commissions than traditional brokers.
- Negotiate with your financial advisor: If you use a financial advisor, negotiate their fees to ensure they are reasonable.
- Consider robo-advisors: Robo-advisors are online platforms that provide automated investment management services at a low cost.
By understanding the different types of fees and taking steps to minimize them, you can maximize your investment returns over time. Remember, even small fees can add up significantly over the long term, so it’s important to be aware of them and take action to reduce them whenever possible.
Choosing Low-Cost Investment Options
Investing can be a daunting task, especially for those new to the financial world. One of the biggest obstacles is the perception that investing requires a large sum of money. However, this is a misconception. There are many low-cost investment options available that are accessible to everyone, regardless of their income level.
One of the most popular and accessible options is investing in mutual funds. Mutual funds allow investors to pool their money together and invest in a diversified portfolio of stocks, bonds, or other assets. They are managed by professional fund managers who make investment decisions on behalf of the investors. The fees associated with mutual funds vary, but many offer low-cost options, especially index funds that track a specific market index.
Another option is exchange-traded funds (ETFs). ETFs are similar to mutual funds, but they trade on stock exchanges like individual stocks. They offer a wide range of investment options, from broad market ETFs to sector-specific ETFs. ETFs are generally considered more cost-effective than mutual funds, with lower expense ratios and trading fees.
For those who prefer a more hands-on approach, online brokerage accounts provide a platform to buy and sell individual stocks, bonds, and other securities. Many online brokerages offer commission-free trades, making them an affordable option for active investors. However, it’s crucial to conduct thorough research and understand the risks involved before investing in individual securities.
Robo-advisors are another emerging investment option that has gained popularity in recent years. These automated investment platforms use algorithms to create and manage portfolios based on investors’ risk tolerance and financial goals. Robo-advisors typically charge low fees and are a good option for investors who prefer a hands-off approach.
Choosing the right low-cost investment option depends on your individual circumstances, investment goals, and risk tolerance. It’s essential to do your research and compare different options before making any investment decisions. By understanding the available choices and their associated fees, you can make informed decisions that align with your financial aspirations.
Exploring Index Funds and ETFs
In the world of investing, index funds and exchange-traded funds (ETFs) have gained immense popularity as accessible and diversified investment options. These funds track the performance of specific market indexes, offering investors a convenient way to gain exposure to a broad range of assets.
Let’s delve into the key aspects of index funds and ETFs, understanding their similarities, differences, and how they can contribute to your investment portfolio.
What are Index Funds?
Index funds are mutual funds that aim to mirror the performance of a specific market index, such as the S&P 500 or the Nasdaq 100. They achieve this by holding a portfolio of stocks that closely replicates the underlying index’s composition.
Key features of index funds include:
- Passive investment strategy: Index funds employ a passive investment approach, meaning they don’t actively try to outperform the market. Instead, they simply track the index’s performance.
- Diversification: By holding a wide range of securities, index funds provide diversification, reducing risk and minimizing the impact of individual stock fluctuations.
- Low expense ratios: Compared to actively managed funds, index funds generally have lower expense ratios, as they require less management and research.
What are ETFs?
ETFs, or exchange-traded funds, are similar to index funds but are traded on stock exchanges like individual stocks. They represent a basket of underlying assets, often tracking a specific index, commodity, or sector.
Here are some key characteristics of ETFs:
- Traded on exchanges: Unlike mutual funds, ETFs can be bought and sold throughout the trading day on stock exchanges.
- Transparency: ETFs typically have transparent holdings, making it easy for investors to understand the underlying assets.
- Tax efficiency: ETFs generally have lower tax implications than mutual funds, as they typically generate fewer taxable events.
Index Funds vs. ETFs: Key Differences
While both index funds and ETFs share similarities, there are some notable differences:
| Feature | Index Fund | ETF |
|---|---|---|
| Trading | Traded once a day at the end of the trading day | Traded throughout the day on exchanges |
| Fees | Typically have lower expense ratios | May have higher expense ratios, but often lower trading commissions |
| Tax efficiency | Can generate higher tax liabilities | Generally more tax-efficient |
| Liquidity | Less liquid than ETFs | More liquid, traded on exchanges |
Choosing Between Index Funds and ETFs
The choice between index funds and ETFs depends on individual investment goals, risk tolerance, and trading preferences. Here are some factors to consider:
- Investment horizon: If you’re investing for the long term, the lower expense ratios of index funds might be more advantageous. For shorter-term trading, the liquidity and intraday trading capabilities of ETFs could be preferred.
- Trading frequency: If you plan to trade frequently, ETFs offer more flexibility and intraday price adjustments. Index funds, with their once-a-day valuation, might be better suited for infrequent trading.
- Tax implications: ETFs can offer greater tax efficiency, especially for investors in higher tax brackets.
Conclusion
Index funds and ETFs provide a valuable and accessible way to invest in the market. They offer diversification, low expenses, and transparency, making them suitable for a wide range of investors. Whether you choose index funds or ETFs, understanding their key features and how they align with your investment objectives is essential for making informed decisions.
Negotiating Fees with Financial Advisors
Finding the right financial advisor can be a daunting task, but once you find one you trust, it’s crucial to discuss fees and ensure a transparent understanding of their compensation structure. Negotiating fees is an essential part of the process, as it allows you to get the best value for your investment and ensure you’re comfortable with the costs associated with their services.
Here are some key tips for negotiating fees with financial advisors:
1. Research Different Fee Structures
Financial advisors use various fee structures. Common ones include:
- Fee-only advisors: Charge a fixed fee based on the services provided, typically an hourly rate or a percentage of assets under management (AUM).
- Commission-based advisors: Earn commissions on products they sell, such as insurance or investment products.
- Fee-based advisors: Charge both a fee for their services and commissions on products they sell.
Understanding the different fee structures and their implications will help you compare advisors and determine the best fit for your financial goals and risk tolerance.
2. Be Clear About Your Expectations
Before your meeting, clearly define your needs and expectations. What services do you require? What is your investment timeframe and risk tolerance? Having a clear understanding of your goals will help you determine the level of service you need and the fees associated with it.
3. Ask the Right Questions
Don’t be afraid to ask detailed questions about the advisor’s fees and compensation structure. Ask:
- What are your fees? (be specific – hourly, percentage of AUM, etc.)
- Are there any additional fees? (e.g., trading fees, account maintenance fees)
- What is your minimum investment requirement?
- Are there any performance-based fees?
- What are the terms of the agreement? (e.g., termination fees, duration of the agreement)
4. Don’t Be Afraid to Negotiate
Financial advisors are professionals, but they are also business owners. They understand the value of their services, but they are also open to negotiations, especially for clients with substantial assets. Be polite but firm when discussing fees. If you find their fees too high, don’t be afraid to negotiate. You can always explore other options or look for alternative fee structures. Explain your specific needs and see if you can find a compromise that suits both parties.
5. Consider the Total Value
Remember that fees aren’t the only factor to consider when choosing a financial advisor. Look at the overall value they provide, including their experience, expertise, and track record. A higher fee might be justified if the advisor can consistently deliver exceptional returns and support your financial goals. Ultimately, finding an advisor who aligns with your values, goals, and investment philosophy is essential.
6. Get It in Writing
Once you’ve negotiated fees and agreed upon a contract, ensure all the terms are clearly defined in writing. This includes the scope of services, fees, compensation structure, and any termination clauses. This document will serve as a reference point and safeguard your interests throughout the relationship.
Negotiating fees with financial advisors can be a crucial step in securing the best possible financial guidance and ensuring you’re comfortable with the financial aspects of your investment journey. By following these tips, you can approach this conversation confidently and make informed decisions that align with your financial goals and aspirations.
Consider Robo-Advisors for Automated Investing

Robo-advisors have emerged as a popular alternative to traditional financial advisors, offering automated investment management services at a fraction of the cost. These platforms leverage sophisticated algorithms and technology to create personalized investment portfolios tailored to your financial goals and risk tolerance.
One of the key benefits of robo-advisors is their affordability. Unlike traditional advisors who charge high fees based on the assets under management, robo-advisors typically charge low annual fees, often less than 1%. This makes them an attractive option for investors of all income levels, especially those with smaller investment portfolios.
Another advantage is their convenience and accessibility. Robo-advisors are available online 24/7, allowing you to manage your investments from anywhere with an internet connection. They also provide user-friendly interfaces and educational resources to help you understand your investment strategy.
Robo-advisors also excel in diversification. By using algorithms to allocate your investments across different asset classes, such as stocks, bonds, and real estate, they help minimize risk and potentially maximize returns. This automated process ensures that your portfolio is constantly rebalanced to maintain your desired asset allocation.
While robo-advisors offer many advantages, it’s important to note that they are not a perfect solution for everyone. They may not be suitable for investors with complex financial needs or those seeking personalized advice from a human advisor.
In conclusion, robo-advisors provide a convenient, affordable, and automated way to manage your investments. If you’re looking for a hands-off approach to investing with a focus on diversification and low fees, consider exploring the world of robo-advisors.
Reviewing and Monitoring Investment Fees Regularly
In the world of investing, it’s easy to get caught up in the excitement of potential returns. But it’s crucial to remember that every investment comes with costs, including fees. These fees can significantly impact your overall returns, so it’s essential to review and monitor them regularly.
Why are Investment Fees Important?
Investment fees can come in various forms, such as:
- Management fees: Charged by fund managers for overseeing your investments.
- Transaction fees: Incurred when buying or selling securities.
- Advisory fees: Paid to financial advisors for their guidance and recommendations.
- Platform fees: Charged by online brokerage platforms for using their services.
These fees may seem small individually, but they can add up over time and eat into your investment gains. For instance, a 1% annual management fee on a $100,000 portfolio equates to $1,000 per year, which is a significant amount of money.
How to Review and Monitor Investment Fees:
Here are some practical steps to ensure you’re not paying excessive fees:
- Understand the Fee Structure: Before investing, carefully read the prospectus or fund documents to understand the fees associated with each investment.
- Compare Fees: Don’t just settle for the first investment option you come across. Compare fees across different funds and investment platforms to find the best deals.
- Track Your Fees Over Time: Regularly track your investment fees and their impact on your overall returns. Consider using a spreadsheet or financial management software to make this process easier.
- Negotiate Fees: If you have a large investment portfolio, consider negotiating lower fees with your fund manager or financial advisor.
The Bottom Line:
By reviewing and monitoring investment fees regularly, you can save money and improve your overall investment returns. It’s essential to be informed and proactive in managing your investment costs to maximize your financial goals.
Minimizing Trading Costs
Trading costs are a significant factor to consider when investing in the stock market. They can eat into your profits and affect your overall returns. Understanding the different types of trading costs and how to minimize them is crucial for any investor, especially those who are just starting out.
Types of Trading Costs
There are several types of trading costs, including:
- Brokerage fees: These are commissions charged by your broker for executing trades. They can be fixed fees per trade, percentage-based fees, or a combination of both.
- Exchange fees: These fees are charged by stock exchanges for facilitating the trading of stocks. They are typically very small, but they add up over time.
- Spread: This is the difference between the bid price (what buyers are willing to pay) and the ask price (what sellers are willing to sell for). The spread represents the profit margin for market makers, and it is another cost that traders have to pay.
- Slippage: This occurs when you place an order at a specific price, but the stock price moves against you before the order is filled. This can happen when there is a lot of market volatility or when the order size is large.
How to Minimize Trading Costs
Here are some tips on how to minimize trading costs:
- Choose a broker with low fees: Compare brokerage fees from different brokers and choose one that offers the lowest fees for your trading style. Some brokers offer free trading for certain types of stocks or ETFs.
- Trade in larger quantities: Larger trades typically have lower per-share costs, so consider consolidating your trades into larger orders when possible.
- Time your trades carefully: Avoid trading during times of high volatility, as this can lead to higher slippage costs. Trading during periods of low liquidity can also result in higher spreads.
- Use limit orders: Limit orders allow you to specify the price at which you want to buy or sell a stock. This helps to avoid paying higher prices than you are willing to, and it can also minimize slippage.
- Consider investing in ETFs: ETFs typically have lower trading costs than individual stocks, as they are traded on exchanges like stocks. They also offer diversification, which can help to reduce risk.
Conclusion
Minimizing trading costs is an important part of investing successfully. By understanding the different types of trading costs and following the tips above, you can save money and maximize your returns over the long term.
The Power of Compounding with Lower Fees
Compounding is one of the most powerful forces in finance. It’s the ability of your investments to grow exponentially over time, thanks to the reinvestment of earnings. The higher the rate of return and the longer the time horizon, the greater the power of compounding. However, one often overlooked factor that can significantly impact the effectiveness of compounding is fees.
Fees can eat into your investment returns, hindering the power of compounding. Consider a simple example: let’s say you invest $10,000 in a mutual fund with an annual return of 10% and an annual expense ratio of 1%. Over 30 years, your investment would grow to approximately $174,494 with the fees. But if the fund had no fees, your investment would grow to a much larger sum, approximately $179,085.
The difference may seem small at first, but over the long term, those seemingly insignificant fees can accumulate and have a significant impact on your overall returns. In this example, the higher fees cost you almost $4,600 in potential earnings. This is just a small illustration, and the impact of fees can be much larger depending on the specific investment and the time horizon.
Why Lower Fees Matter
Lower fees are crucial for maximizing the power of compounding because they allow more of your investment to work for you. When you pay lower fees, more of your money is available to generate returns, which are then reinvested to earn even more. This creates a snowball effect, where your investment grows at an accelerated rate over time.
Strategies for Lowering Fees
Here are some strategies you can use to reduce the impact of fees on your investments:
- Choose low-cost index funds and ETFs: Index funds and ETFs track a specific market index, such as the S&P 500, and typically have lower expense ratios than actively managed funds.
- Invest in direct real estate: While real estate investing can be more complex than traditional investments, it allows you to avoid some of the fees associated with mutual funds and other investment vehicles.
- Consider robo-advisors: Robo-advisors offer automated investment management services at lower fees than traditional advisors.
- Negotiate fees with financial advisors: If you’re working with a financial advisor, don’t be afraid to negotiate fees to ensure you’re getting a good value for their services.
The Bottom Line
Fees are an often overlooked but crucial factor in the power of compounding. By minimizing the impact of fees, you can maximize the growth potential of your investments and achieve your financial goals more efficiently. So, choose investments with low fees and watch your money grow over time.