Retirement may seem like a distant concept in your 20s and 30s, but starting to plan early can make a huge difference in your future financial security. It’s never too early to start planning for your golden years, and in fact, the earlier you start, the more time your money has to grow. By taking proactive steps now, you can set yourself up for a comfortable and fulfilling retirement, even if it seems far off.
This guide will provide you with a comprehensive roadmap for retirement planning in your 20s and 30s. We’ll cover essential topics like setting financial goals, choosing the right retirement accounts, investing strategies, and building healthy financial habits. So, whether you’re just starting your career or already established, this guide will equip you with the knowledge and tools to take control of your future and ensure a secure and enjoyable retirement.
The Importance of Starting Early
Starting early is a valuable habit that can bring numerous benefits to your life. It’s about proactivity, discipline, and taking advantage of opportunities. When you start early, you give yourself a head start, allowing you to achieve more and overcome obstacles with greater ease.
In the realm of academics, starting early can significantly impact your success. By beginning assignments and studying ahead of schedule, you reduce stress and pressure, leaving ample time for understanding concepts and mastering skills. This also allows for better time management and a more balanced academic life.
Starting early also applies to career development. Building a strong foundation early in your career can set you apart from the competition. Gaining valuable experience, developing key skills, and networking with professionals will put you on the path to a successful and fulfilling career.
Moreover, starting early in personal pursuits can lead to remarkable achievements. Whether it’s learning a new language, pursuing a hobby, or starting a side hustle, taking action early on can unlock your potential and open doors to new possibilities.
While starting early might seem daunting at times, remember that it’s all about taking small steps and building momentum. Start with a little bit each day, gradually increasing your efforts as you become more comfortable. The rewards of starting early are immeasurable, leading to greater accomplishment, personal growth, and overall well-being.
Setting Realistic Retirement Goals
Retirement is a significant milestone in life, and it’s essential to have a plan to ensure a comfortable and fulfilling transition. Setting realistic retirement goals is crucial for achieving financial security and enjoying your golden years.
Here’s a step-by-step guide to setting realistic retirement goals:
1. Determine Your Retirement Timeline
Start by deciding when you envision retiring. This will give you a clear timeframe to work with and help you plan accordingly. Consider factors such as your age, health, and desired lifestyle.
2. Estimate Your Expenses
Create a detailed budget that outlines your anticipated expenses in retirement. These may include housing, healthcare, travel, entertainment, and other essential costs. It’s essential to consider inflation and potential healthcare costs.
3. Calculate Your Savings Needs
Based on your expenses and retirement timeline, you can estimate the amount of money you’ll need to save. Several online calculators and financial advisors can assist in this process. A general rule of thumb is to aim for 80% of your pre-retirement income.
4. Set Financial Goals
Establish specific financial goals that align with your retirement aspirations. These could include purchasing a vacation home, traveling the world, or starting a business. Having concrete goals will motivate you to stay on track.
5. Consider Investment Strategies
Develop an investment strategy that balances risk and return. Diversify your portfolio across different asset classes, such as stocks, bonds, and real estate. Consult with a financial advisor to create a personalized plan that aligns with your risk tolerance.
6. Review and Adjust Regularly
Retirement planning is an ongoing process. Regularly review your goals and investment strategy to account for changes in your circumstances or market conditions. Make adjustments as needed to ensure you’re on the right path.
7. Seek Professional Advice
Don’t hesitate to consult with a financial advisor who can provide personalized guidance and support. They can help you create a comprehensive retirement plan that meets your unique needs and aspirations.
Setting realistic retirement goals is a crucial step towards a comfortable and fulfilling retirement. By following these steps, you can increase your chances of achieving financial security and enjoying your golden years.
Estimating Retirement Expenses
Retirement is a significant life milestone, and planning for it is crucial. A crucial aspect of retirement planning is accurately estimating your expenses. Understanding your financial needs during retirement will help you determine how much you need to save, invest, and manage your finances effectively.
Key Factors to Consider
To estimate your retirement expenses, consider the following factors:
- Housing: This is usually the largest expense. Consider your current mortgage payments, property taxes, insurance, and maintenance costs. You might downsize or relocate to a more affordable area in retirement.
- Healthcare: Healthcare costs tend to increase with age. Factor in healthcare premiums, deductibles, copayments, and potential long-term care needs.
- Transportation: Consider the cost of owning or leasing a car, fuel, insurance, and public transportation.
- Food: Account for groceries, dining out, and entertainment expenses related to food.
- Travel: If you plan to travel, factor in airfare, accommodation, and other travel-related costs.
- Hobbies and Leisure: Account for your favorite hobbies, leisure activities, and social engagements.
- Unexpected Expenses: Set aside a contingency fund for unexpected events like home repairs, medical emergencies, or family emergencies.
Tools and Resources
Several resources can help you estimate your retirement expenses:
- Retirement Calculators: Many financial institutions and websites offer online retirement calculators that can estimate your needs based on your income, expenses, and investment goals.
- Financial Advisors: A financial advisor can provide personalized advice and help you create a comprehensive retirement plan.
- Budgeting Apps: Use budgeting apps to track your current spending habits and identify areas where you can cut back.
- Retirement Planning Websites: Websites dedicated to retirement planning offer valuable information, tools, and resources.
Important Considerations
Remember these key considerations when estimating your retirement expenses:
- Inflation: Account for inflation, as the cost of goods and services will likely increase over time.
- Lifestyle Changes: Your lifestyle may change in retirement. You might travel more, pursue hobbies, or spend more time with family.
- Healthcare Costs: Healthcare expenses can be unpredictable. Consider long-term care insurance or other options to manage potential costs.
Conclusion
Estimating your retirement expenses accurately is essential for financial planning. By considering these factors, utilizing available tools, and staying informed, you can create a retirement plan that addresses your needs and helps you achieve your financial goals.
Understanding Different Retirement Savings Plans
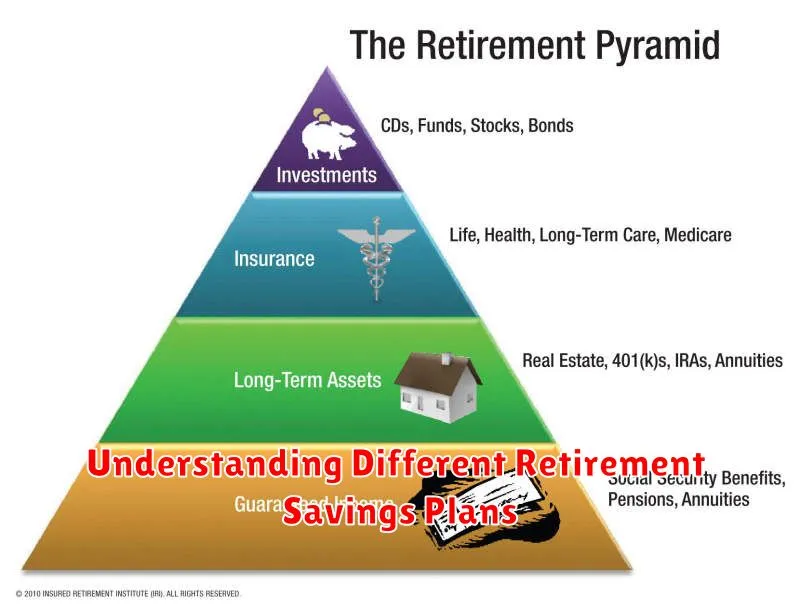
Retirement planning is an essential aspect of financial well-being, and choosing the right retirement savings plan is crucial. There are various retirement savings options available, each with its own features, benefits, and limitations. Understanding the differences between these plans can help you make informed decisions and maximize your retirement savings.
1. Traditional Individual Retirement Account (IRA)
A Traditional IRA is a retirement savings plan that allows individuals to contribute pre-tax dollars to an account that grows tax-deferred. This means you won’t pay taxes on the earnings until you withdraw them in retirement. Traditional IRA contributions may be tax-deductible, reducing your taxable income in the current year. However, withdrawals in retirement will be taxed as ordinary income.
2. Roth IRA
A Roth IRA is another popular retirement savings option. Unlike a Traditional IRA, contributions to a Roth IRA are made with after-tax dollars. This means you won’t receive a tax deduction for your contributions but your withdrawals in retirement will be tax-free. Roth IRAs are particularly beneficial for individuals who expect to be in a higher tax bracket in retirement than they are today.
3. 401(k) Plan
A 401(k) plan is a retirement savings plan offered by employers. Employees can contribute a portion of their salary to the plan, and the employer may match a portion of the contributions. 401(k) contributions are made with pre-tax dollars, reducing your taxable income. Withdrawals in retirement are taxed as ordinary income.
4. 403(b) Plan
A 403(b) plan is similar to a 401(k) plan, but it is typically offered to employees of non-profit organizations, public schools, and certain other tax-exempt employers. Like 401(k) plans, 403(b) contributions are made with pre-tax dollars and grow tax-deferred.
5. Simplified Employee Pension (SEP) IRA
A SEP IRA is a retirement savings plan available to self-employed individuals and small business owners. It allows you to contribute a percentage of your net self-employed income to a traditional IRA. SEP IRA contributions are tax-deductible, reducing your taxable income. Withdrawals in retirement are taxed as ordinary income.
Choosing the Right Retirement Savings Plan
The best retirement savings plan for you depends on your individual circumstances, financial goals, and tax situation. Consider factors such as your age, income, employment status, and expected tax bracket in retirement. It’s also important to consult with a financial advisor to get personalized guidance.
Maximizing Employer-Sponsored Plans
Employer-sponsored plans are a valuable benefit offered by many companies to their employees. These plans can include health insurance, retirement savings plans, and other perks. By maximizing your participation in these plans, you can save money, improve your financial security, and enhance your overall well-being.
Health Insurance
Health insurance is a crucial component of any employee benefits package. It provides financial protection against the high cost of healthcare. When choosing a health insurance plan, consider your individual needs and budget. Take advantage of open enrollment periods to review and update your coverage.
Important Tips:
- Understand the different types of plans available, such as health maintenance organizations (HMOs), preferred provider organizations (PPOs), and high-deductible health plans (HDHPs).
- Compare the premiums, deductibles, copayments, and out-of-pocket maximums for each plan.
- Consider your health history and anticipated healthcare needs.
Retirement Savings Plans
Retirement savings plans, such as 401(k)s and 403(b)s, allow you to save for retirement on a pre-tax basis. Many employers offer matching contributions, which means they will match a certain percentage of your contributions. Take full advantage of employer matching programs to maximize your retirement savings.
Important Tips:
- Contribute the maximum amount allowed by your plan.
- Diversify your investments across different asset classes, such as stocks, bonds, and real estate.
- Review your investment allocation periodically and make adjustments as needed.
Other Employer-Sponsored Benefits
In addition to health insurance and retirement savings plans, employers may offer a variety of other benefits, such as:
- Life insurance
- Disability insurance
- Paid time off
- Tuition reimbursement
- Employee assistance programs (EAPs)
Take the time to understand and utilize these benefits to your advantage. They can provide valuable financial and personal support throughout your career.
Conclusion
Maximizing your participation in employer-sponsored plans can significantly improve your financial well-being. By making informed decisions about your health insurance, retirement savings, and other benefits, you can secure your future and enhance your overall quality of life.
Exploring Individual Retirement Accounts (IRAs)
Saving for retirement is crucial, and Individual Retirement Accounts (IRAs) are a valuable tool to help you reach your financial goals. IRAs offer tax advantages and flexibility, making them a popular choice for many individuals. In this article, we will delve into the different types of IRAs, their benefits, and how they can work for you.
Types of IRAs
There are two primary types of IRAs: Traditional IRAs and Roth IRAs. The main difference between them lies in how they are taxed.
Traditional IRA
With a Traditional IRA, you contribute pre-tax dollars, which means you deduct your contributions from your taxable income. You won’t pay taxes on the money until you withdraw it in retirement. This can be beneficial if you expect to be in a lower tax bracket in retirement than you are currently.
Roth IRA
On the other hand, a Roth IRA uses after-tax contributions, meaning you’ve already paid taxes on the money you put into the account. When you withdraw your funds in retirement, you’ll do so tax-free. This can be advantageous if you expect to be in a higher tax bracket in retirement.
Benefits of IRAs
Both Traditional and Roth IRAs offer numerous benefits, including:
- Tax advantages: IRAs provide tax benefits, either through tax deductions (Traditional IRA) or tax-free withdrawals (Roth IRA).
- Flexibility: You can choose how you invest your IRA contributions, giving you control over your retirement savings.
- Potential for growth: Your investments can grow tax-deferred (Traditional IRA) or tax-free (Roth IRA), allowing your retirement savings to compound over time.
- Protection from creditors: IRA assets are generally protected from creditors in most circumstances.
How to Choose the Right IRA
The best IRA for you depends on your individual circumstances, including your current income, expected future income, and tax bracket. It’s essential to consider factors such as:
- Your current tax bracket and your anticipated tax bracket in retirement.
- Your financial goals and time horizon for retirement.
- Your risk tolerance and investment preferences.
Contributing to an IRA
There are annual contribution limits for IRAs. For 2023, the maximum contribution for both Traditional and Roth IRAs is $6,500 for individuals under age 50 and $7,500 for those 50 and older. You can contribute to both a Traditional IRA and a Roth IRA, but the total contribution cannot exceed the annual limit.
Conclusion
IRAs are a powerful tool for retirement planning. Whether you choose a Traditional or Roth IRA, they provide tax advantages, flexibility, and potential for growth. By understanding the different types of IRAs and their benefits, you can make informed decisions about your retirement savings and work towards a financially secure future.
It’s always advisable to consult with a financial advisor to determine the best IRA strategy for your specific needs and goals.
Investing for Long-Term Growth

Investing for the long term is a crucial aspect of achieving financial security and reaching your financial goals. It involves a strategic approach that emphasizes patience, consistency, and a focus on long-term growth rather than short-term gains.
The key to successful long-term investing lies in understanding the principles of compounding and time value of money. Compounding is the process where investment returns generate further returns over time, creating a snowball effect. The longer you invest, the more significant the impact of compounding becomes. Time value of money highlights the concept that money available today is worth more than the same amount of money in the future, due to its potential earning capacity.
When investing for the long term, it is essential to prioritize diversification. Diversifying your portfolio across different asset classes, such as stocks, bonds, real estate, and commodities, helps reduce risk and potentially increase returns. By spreading your investments, you mitigate the impact of any single asset’s performance on your overall portfolio.
Another vital aspect of long-term investing is patience. It is important to resist the temptation to react to market fluctuations or short-term trends. Long-term investors remain focused on their investment goals and maintain a disciplined approach, even in the face of market volatility. They understand that the stock market experiences ups and downs, and they are prepared to ride out the inevitable fluctuations.
Furthermore, regular investing is crucial for long-term growth. Consistent contributions to your investment portfolio, even in small amounts, can significantly compound over time. By establishing a disciplined savings and investing plan, you can harness the power of compounding and gradually accumulate wealth.
Investing for long-term growth requires a well-defined strategy, patience, discipline, and a focus on compounding. By adhering to these principles, you can navigate the complexities of the investment world and work towards achieving your financial objectives over the long term.
Managing Debt and Building Good Credit
Managing debt and building good credit are essential aspects of financial well-being. By taking proactive steps to understand and manage your finances, you can establish a strong foundation for future financial success.
Understanding Debt
Debt can be a powerful tool when used responsibly. However, excessive debt can lead to financial stress and hinder your ability to achieve your financial goals. It’s crucial to differentiate between good debt and bad debt.
Good Debt
Good debt is typically associated with investments that have the potential to generate future income or increase your asset value. Examples include:
- Student loans for education that leads to higher earning potential
- Mortgages for purchasing a home that appreciates in value over time
- Business loans for starting or expanding a profitable venture
Bad Debt
Bad debt refers to debt that accrues high interest rates and does not provide a significant return on investment. Examples include:
- Payday loans with exorbitant interest charges
- Credit card debt with high annual percentage rates (APRs)
- Cash advances that often carry substantial fees
Building Good Credit
Good credit is a reflection of your financial responsibility and trustworthiness. Lenders use your credit score to assess your creditworthiness and determine the interest rates and loan terms they offer. Here are some key strategies for building good credit:
1. Pay Your Bills On Time
Prompt payment demonstrates your ability to manage your finances effectively. Late payments can negatively impact your credit score, so it’s essential to make timely payments on all your bills.
2. Use Credit Responsibly
Avoid maxing out your credit cards and aim to keep your credit utilization ratio (the amount of credit you’re using compared to your total credit limit) low. A higher utilization ratio can indicate that you’re heavily reliant on credit and can negatively affect your score.
3. Diversify Your Credit
Having a mix of different credit accounts, such as credit cards, installment loans, and mortgages, can demonstrate your ability to manage various types of credit responsibly. This can contribute to a higher credit score.
4. Monitor Your Credit Report
It’s crucial to regularly review your credit report for any errors or inconsistencies. You can obtain free credit reports from the three major credit bureaus: Experian, Equifax, and TransUnion.
Conclusion
Managing debt and building good credit are ongoing processes that require discipline and awareness. By understanding the principles of responsible credit management and implementing the strategies outlined above, you can establish a strong financial foundation and achieve your financial goals.
Regularly Review and Adjust Your Plan
A plan is only as good as its execution, and even the best-laid plans can go awry. Life is dynamic and unpredictable, and your goals and circumstances will inevitably change over time. To ensure your plan remains relevant and effective, it’s crucial to regularly review and adjust it.
Think of your plan as a living document, not a static blueprint. Set aside dedicated time to revisit your goals and strategies. Evaluate your progress, identify any roadblocks or unforeseen challenges, and make necessary adjustments to your course of action.
Regular review can involve a simple check-in with yourself, or a more formal process with specific metrics and feedback mechanisms. The frequency of your reviews will depend on your individual needs and the complexity of your plan. For example, you might review your financial plan quarterly, while your fitness plan might require weekly adjustments.
By actively managing your plan, you remain proactive in achieving your goals. You can course-correct before problems become insurmountable, capitalize on emerging opportunities, and ensure your plan remains aligned with your evolving priorities. Regularly reviewing and adjusting your plan is an investment in your success.

