Are you considering making investments but feeling unsure about how capital gains taxes will impact your overall wealth strategy? Understanding capital gains taxes is crucial for anyone looking to build long-term wealth. These taxes, levied on profits made from selling assets like stocks, bonds, and real estate, can significantly affect your returns. While they are a necessary component of the tax system, their impact shouldn’t be overlooked when crafting your investment plan.
This article will delve into the intricacies of capital gains taxes and their implications for your wealth strategy. We’ll explore different tax brackets, holding periods, and strategies for minimizing your tax burden. Whether you’re a seasoned investor or just starting, understanding how capital gains taxes work is essential for making informed decisions that can help you achieve your financial goals.
What are Capital Gains Taxes?
Capital gains taxes are taxes on the profit you make when you sell an asset for more than you paid for it. The asset can be anything from stocks and bonds to real estate and artwork. The profit you make on the sale is called a capital gain.
Capital gains taxes are a part of the federal income tax system, and they are also taxed at the state level in some states. The rate at which capital gains are taxed depends on several factors, including your income level, how long you’ve owned the asset, and whether it was a long-term or short-term gain.
For example, if you sell an asset that you’ve owned for more than a year, you’ll pay a lower tax rate on the profit than if you sold it after owning it for less than a year. This is because short-term capital gains are taxed at your ordinary income tax rate, while long-term capital gains are taxed at a lower rate.
Capital gains taxes can be a complex topic. If you are considering selling an asset that you believe may result in a capital gain, it is important to consult with a tax professional to make sure you understand your tax obligations.
Short-Term vs. Long-Term Capital Gains: Understanding the Difference
When you sell an asset for a profit, you’ve realized a capital gain. The way this gain is taxed depends on how long you’ve held the asset. This is where the distinction between short-term and long-term capital gains comes in.
Here’s a breakdown of the two:
Short-Term Capital Gains
Short-term capital gains occur when you sell an asset that you’ve held for less than one year. These gains are taxed at your ordinary income tax rate, which can be as high as 37% for the highest earners.
Long-Term Capital Gains
Long-term capital gains occur when you sell an asset you’ve held for one year or more. These gains are taxed at preferential rates, which are lower than ordinary income tax rates. Currently, the long-term capital gains tax rates are:
- 0% for taxpayers in the 10% or 12% ordinary income tax brackets
- 15% for most other taxpayers
- 20% for taxpayers in the highest income bracket
Example
Let’s say you bought 100 shares of XYZ stock for $50 per share in January 2022. In November 2022, you sell those shares for $75 per share. You’ve made a profit of $25 per share, or $2,500 total. Since you held the shares for less than a year, this would be considered a short-term capital gain and taxed at your ordinary income tax rate.
Now, imagine you held those same shares until November 2023. Since you held them for over a year, you’d realize a long-term capital gain, which would be taxed at the preferential rates mentioned above.
Key Takeaways
Understanding the difference between short-term and long-term capital gains is crucial for tax planning. If you’re considering selling an asset, it’s important to factor in the holding period to determine how your profit will be taxed.
By carefully planning your investment strategies, you can potentially reduce your tax burden and maximize your investment returns.
How Capital Gains Taxes Affect Your Investment Decisions

Capital gains taxes are a significant factor to consider when making investment decisions. They are taxes levied on profits realized from the sale of an asset, such as stocks, bonds, or real estate. Understanding how these taxes work can help you make informed investment choices that maximize your returns and minimize your tax liability.
Understanding Capital Gains Taxes
Capital gains are classified as either short-term or long-term, depending on how long you held the asset before selling it.
- Short-term capital gains are realized from assets held for less than one year. They are taxed at your ordinary income tax rate, which can range from 10% to 37% depending on your income level.
- Long-term capital gains are realized from assets held for more than one year. These gains are generally taxed at lower rates than ordinary income, with rates ranging from 0% to 20% depending on your income level.
How Capital Gains Taxes Affect Your Investment Decisions
Capital gains taxes can influence your investment decisions in several ways:
- Holding Period: Holding an asset for longer than one year can qualify you for the lower long-term capital gains tax rate. This can incentivize investors to hold assets for longer periods, even if short-term opportunities exist.
- Investment Strategy: Investors may adjust their investment strategies to minimize their tax liability. For example, they may choose to invest in assets that are expected to generate long-term gains, or they may use tax-loss harvesting to offset capital gains.
- Trading Frequency: Frequent trading can generate significant capital gains, which can be subject to higher tax rates. Investors may choose to trade less frequently to minimize their tax exposure.
- Asset Allocation: The tax implications of different asset classes can affect how investors allocate their portfolios. For instance, investors may favor assets with lower capital gains tax rates, such as real estate.
Tax Planning Strategies
There are several tax planning strategies that can help you minimize your capital gains taxes:
- Tax-Loss Harvesting: This strategy involves selling losing investments to offset capital gains. This can help reduce your overall tax liability.
- Tax-Advantaged Accounts: Investing in retirement accounts like 401(k)s and IRAs can help defer capital gains taxes until retirement.
- Consult a Tax Professional: It’s important to consult with a qualified tax professional to understand your specific tax situation and explore ways to minimize your tax burden.
Conclusion
Capital gains taxes are a crucial factor to consider when making investment decisions. By understanding the tax implications of your investments and utilizing tax planning strategies, you can maximize your returns and minimize your tax liability. Consulting with a financial advisor or tax professional can help you develop a comprehensive investment strategy that aligns with your individual circumstances and tax goals.
Strategies for Minimizing Capital Gains Tax Liability
Capital gains tax is a tax levied on the profit realized from the sale of an asset, such as stocks, bonds, real estate, or other investments. This tax can be a significant expense, especially for investors who have realized large gains. Fortunately, there are several strategies you can employ to minimize your capital gains tax liability.
1. Utilize Tax-Advantaged Accounts
Investing in tax-advantaged accounts like Individual Retirement Accounts (IRAs) and 401(k)s allows your investments to grow tax-deferred, meaning you won’t owe taxes on your gains until you withdraw the money in retirement. This can significantly reduce your overall tax burden.
2. Harvest Losses to Offset Gains
If you’ve experienced losses in your investment portfolio, you can use those losses to offset any capital gains you’ve realized. This strategy is known as tax-loss harvesting. By selling losing investments and realizing the losses, you can reduce your taxable capital gains, potentially even eliminating them entirely.
3. Long-Term Capital Gains vs. Short-Term Capital Gains
The tax rate you pay on capital gains depends on how long you’ve held the asset. Long-term capital gains, which are realized from assets held for more than one year, are generally taxed at a lower rate than short-term capital gains, which are realized from assets held for one year or less. If you can, try to hold onto your investments for longer than a year to benefit from the lower tax rate.
4. Charitable Donations of Appreciated Assets
Donating appreciated assets, such as stocks or real estate, to charity can provide a double tax advantage. You can deduct the fair market value of the asset as a charitable donation, and you avoid paying capital gains tax on the appreciation. This strategy can be particularly beneficial for high-net-worth individuals.
5. Consult with a Financial Advisor
Navigating capital gains taxes can be complex, and it’s always a good idea to consult with a qualified financial advisor to develop a personalized tax strategy. They can help you identify the best options for your situation and ensure you’re taking full advantage of all available tax benefits.
Minimizing capital gains tax liability is an important consideration for any investor. By utilizing the strategies outlined above, you can reduce your tax burden and maximize your investment returns. Remember, seeking professional financial advice can help you make informed decisions and optimize your tax strategies.
Tax-Loss Harvesting: Turning Losses into Opportunities
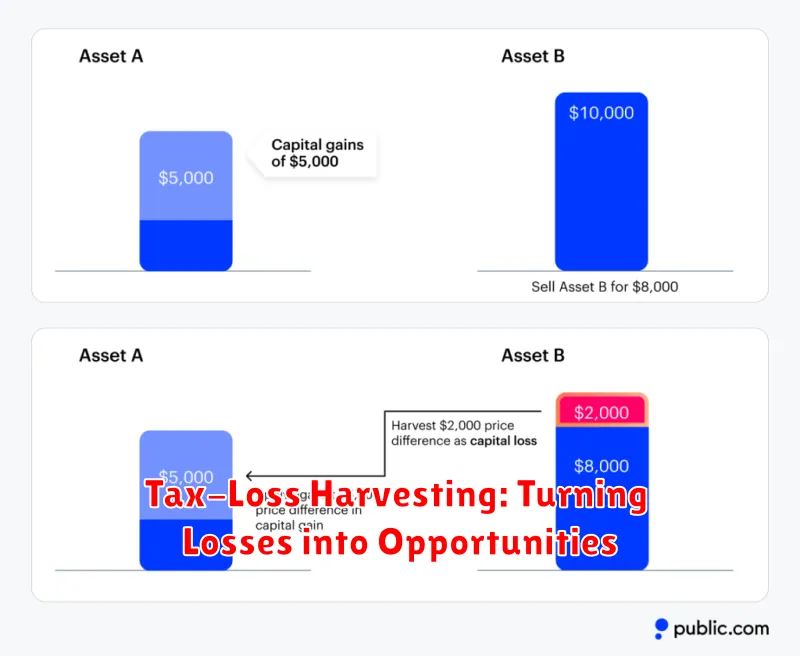
In the world of investing, it’s inevitable that you’ll encounter both gains and losses. While we all strive for positive returns, sometimes market fluctuations or poor investment decisions can lead to losses. However, there’s a strategy called tax-loss harvesting that can help you turn those losses into potential opportunities.
Tax-loss harvesting is a technique that involves selling losing investments to realize a capital loss, which can then be used to offset capital gains on other investments. This strategy can reduce your overall tax burden, freeing up more of your investment dollars to grow over time.
How Tax-Loss Harvesting Works
Imagine you invested in a stock that has lost value. Instead of holding onto it hoping it will rebound, you decide to sell it. By selling the stock at a lower price than your purchase price, you’ve incurred a capital loss. This loss can be used to offset any capital gains you may have realized from other investments during the year.
For example, if you sold a stock for $5,000 that you originally bought for $10,000, you would have a $5,000 capital loss. If you also sold another stock for $12,000 that you bought for $8,000, resulting in a $4,000 capital gain, you can use the $5,000 loss to offset the $4,000 gain. This would reduce your taxable capital gains by $4,000.
Benefits of Tax-Loss Harvesting
Tax-loss harvesting offers several benefits, including:
- Tax Savings: By offsetting capital gains, you can reduce your overall tax liability.
- Increased Investment Growth: The tax savings you realize can be reinvested, potentially leading to higher returns over the long term.
- Flexibility: You can choose to sell losing investments in any tax year, giving you flexibility in managing your tax obligations.
Considerations and Limitations
While tax-loss harvesting can be a valuable strategy, there are a few important considerations:
- Wash Sale Rule: If you repurchase the same or substantially identical securities within 30 days of selling them at a loss, the IRS considers it a wash sale and disallows the loss deduction.
- Investment Horizon: Tax-loss harvesting is generally most effective for long-term investors, as it requires patience and a willingness to manage your portfolio strategically.
- Market Volatility: In volatile markets, it can be challenging to identify and sell losing investments at the right time.
Conclusion
Tax-loss harvesting is a smart tax planning strategy that can help investors minimize their tax burden and maximize their investment returns. By carefully considering the benefits and limitations, you can make informed decisions about how to implement this strategy for your own portfolio.
It’s always a good idea to consult with a qualified financial advisor to discuss tax-loss harvesting and other investment strategies that may be suitable for your specific circumstances.
The Impact of Capital Gains on Real Estate Investments
Capital gains are the profits realized from the sale of an asset, such as real estate. They are a significant factor to consider when investing in real estate, as they can have a major impact on your overall return. Understanding the implications of capital gains can help you make informed decisions about your real estate investments.
Capital Gains Tax
When you sell a property, you may be subject to capital gains tax. This tax is levied on the profit you make from the sale, which is calculated as the difference between the sale price and your original purchase price, plus any improvements you made to the property. The amount of capital gains tax you pay will depend on your individual circumstances, including your tax bracket and the length of time you owned the property.
Holding Period
The length of time you hold a property can have a significant impact on your capital gains tax liability. In the United States, if you hold a property for more than a year, you qualify for long-term capital gains tax rates, which are generally lower than short-term capital gains tax rates. This is a crucial factor to consider when determining your investment strategy.
Tax Advantages
Despite the potential for capital gains tax, there are several tax advantages associated with real estate investments. For example, you may be able to deduct certain expenses from your capital gains, such as depreciation, mortgage interest, and property taxes. Additionally, you may be able to defer capital gains tax by reinvesting your profits in other real estate properties through a 1031 exchange. Consult with a tax advisor to understand the specific advantages available to you.
Impact on Returns
Capital gains tax can have a direct impact on your overall return on investment. While it is important to consider potential tax liabilities, it is also crucial to analyze the long-term potential of a real estate investment. By carefully considering factors such as property appreciation, rental income, and potential tax deductions, you can make informed decisions that align with your financial goals.
Conclusion
Capital gains play a significant role in real estate investments. Understanding the implications of capital gains tax, holding periods, and tax advantages can help you make informed decisions that maximize your profits and minimize your tax liabilities. It is always advisable to consult with a financial advisor or tax professional to assess your individual circumstances and develop a comprehensive investment strategy.
Planning for Capital Gains in Retirement
Retirement is a time to enjoy the fruits of your labor, but it can also be a time of significant tax obligations, especially if you’ve accumulated a substantial investment portfolio. One of the most common tax issues retirees face is capital gains tax, which is levied on profits realized from the sale of assets like stocks, bonds, or real estate. Properly planning for capital gains in retirement can help you minimize your tax burden and maximize your enjoyment of your hard-earned savings.
Understanding Capital Gains Tax
Capital gains tax is a federal tax on the profit you make when you sell an asset for more than you paid for it. The tax rate depends on your holding period and your overall income. Short-term capital gains, from assets held for less than a year, are taxed at your ordinary income tax rate. Long-term capital gains, from assets held for a year or more, are taxed at preferential rates, currently ranging from 0% to 20% depending on your income level.
Strategies for Managing Capital Gains in Retirement
There are several strategies you can use to manage capital gains tax during retirement:
- Tax-Loss Harvesting: This strategy involves selling losing investments to offset capital gains from winning investments. This can help reduce your overall tax liability.
- Tax-Efficient Portfolio Design: Constructing a portfolio with a mix of assets that have different tax characteristics can help minimize capital gains exposure. For example, you could include a mix of stocks, bonds, and real estate.
- Roth Conversions: If you have a traditional IRA or 401(k), you can consider converting some or all of it to a Roth IRA. This will allow you to withdraw your money tax-free in retirement, even if it includes capital gains.
- Qualified Charitable Distributions (QCD): If you are 70 ½ or older, you can make direct charitable donations from your IRA without incurring any capital gains tax.
Consult with a Financial Advisor
It’s crucial to consult with a qualified financial advisor who can help you develop a personalized retirement plan that takes into account your specific financial situation and tax goals. They can help you understand the intricacies of capital gains tax and recommend strategies to optimize your retirement income and minimize your tax burden.
By proactively planning for capital gains in retirement, you can enjoy your golden years with peace of mind, knowing that you’re maximizing your income and minimizing your tax liability.
Conclusion: Making Informed Investment Decisions
Investing can be a daunting task, but by understanding the fundamentals and taking a strategic approach, you can make informed decisions that align with your financial goals. It is crucial to carefully consider your risk tolerance, time horizon, and investment objectives before making any investment choices.
Remember that diversification is key to mitigating risk. Spreading your investments across different asset classes, such as stocks, bonds, and real estate, can help to cushion the impact of market fluctuations. Additionally, it is essential to stay informed about market trends and economic conditions, as this knowledge can guide your investment strategy.
Investing requires patience and discipline. Don’t be swayed by short-term market movements or panic-driven decisions. Instead, focus on your long-term goals and stick to your investment plan. Regular monitoring and adjustments may be necessary, but resist the temptation to make impulsive changes.
Lastly, seeking advice from a qualified financial advisor can provide valuable insights and guidance. A professional can help you develop a personalized investment plan, manage your portfolio, and navigate the complex world of finance.
By following these principles, you can enhance your chances of achieving your financial objectives and securing a brighter financial future. Remember, investing is a journey, not a sprint. With careful planning, informed decision-making, and a long-term perspective, you can build a solid investment portfolio that supports your goals and aspirations.

