Planning for retirement is a crucial aspect of financial well-being, and it’s never too early to start. As you approach your golden years, you’ll need a reliable income stream to sustain your lifestyle. While personal savings and investments play a significant role, Social Security stands as a cornerstone of retirement planning for millions of Americans. This government-backed program provides a vital safety net, offering a predictable monthly income that helps bridge the gap between your working years and retirement.
Understanding the ins and outs of Social Security is essential for making informed decisions about your retirement future. From claiming strategies to maximizing benefits, there’s a lot to consider. This article will delve into the crucial role of Social Security in retirement planning, exploring how it works, how it can impact your finances, and what steps you can take to make the most of this valuable program.
How Social Security Works
Social Security is a federal insurance program that provides benefits to retired workers, people with disabilities, and the survivors of deceased workers. It’s funded by payroll taxes paid by workers and their employers.
To qualify for Social Security retirement benefits, you must have worked and paid Social Security taxes for at least 10 years. The amount of your benefits is based on your average earnings over your working years.
Social Security benefits are not free. They are funded by payroll taxes that are deducted from your paycheck. These taxes are used to pay benefits to current retirees and disabled workers, as well as to build up a trust fund to pay for future benefits.
The Social Security program is designed to provide a safety net for workers who are unable to work due to retirement, disability, or death. It’s an important part of the financial security of millions of Americans.
Eligibility Requirements for Benefits
To be eligible for benefits, you must meet certain requirements. These requirements may vary depending on the type of benefit you are applying for. However, some general requirements include:
- You must be a U.S. citizen or a lawful permanent resident.
- You must be working or have worked in the past.
- You must be unemployed through no fault of your own.
- You must be actively seeking work.
In addition to these general requirements, you may also need to meet specific requirements, such as:
- Having a certain amount of work history.
- Earning a certain income.
- Being disabled.
- Being a veteran.
If you are unsure whether you are eligible for benefits, you can contact the relevant agency or organization to learn more. It is important to note that eligibility requirements may change, so it is always best to check with the agency or organization before you apply.
Understanding Your Social Security Statement
Your Social Security statement is a valuable document that provides crucial information about your future retirement benefits. It’s essential to understand the details of your statement and make informed decisions regarding your financial planning.
Key Information on Your Statement
The Social Security statement includes:
- Your Estimated Retirement Benefits: This section shows the monthly benefit you can expect to receive at different retirement ages. The earlier you claim benefits, the lower your monthly payment will be, and vice versa.
- Your Earnings History: This section displays your annual earnings for every year you have worked since you turned 21. It’s essential to ensure all your earnings are reported accurately, as they directly impact your benefits.
- Your Benefit Estimates: The statement provides estimated benefits based on your current earnings and anticipated future earnings. It’s important to note that these are just estimations, and your actual benefits may vary.
- Your Statement Summary: This section provides a brief overview of your estimated benefits and how they are calculated.
- Information on Disability and Survivor Benefits: The statement also includes information on disability and survivor benefits you may be eligible for.
How to Access Your Statement
You can access your Social Security statement online through the Social Security Administration website (ssa.gov). You can also request a paper copy by mail or by phone.
Why Your Statement Matters
Understanding your Social Security statement is crucial for several reasons:
- Financial Planning: It allows you to estimate your future retirement income and plan accordingly.
- Retirement Age Decision: The statement provides information on how claiming benefits at different ages will impact your monthly payments.
- Error Detection: Review your earnings history regularly to ensure accuracy and report any discrepancies to the SSA.
- Disability and Survivor Benefits: It provides information about potential benefits in case of disability or death.
Tips for Reviewing Your Statement
When reviewing your Social Security statement, consider the following:
- Check for Accuracy: Verify that all your earnings are reported correctly.
- Compare Benefit Estimates: Analyze your benefit estimates at different retirement ages to determine the best option for you.
- Plan for Retirement: Factor your Social Security benefits into your overall retirement plan and consider additional savings.
- Consult with a Financial Advisor: A financial advisor can help you understand your statement and create a personalized retirement plan.
Your Social Security statement is an important tool for understanding your future retirement income. By carefully reviewing and understanding its contents, you can make informed financial decisions and plan for a secure retirement.
Estimating Your Retirement Benefits

Retirement planning is a crucial aspect of financial well-being. It involves careful consideration of your financial goals, lifestyle preferences, and potential retirement income sources. One of the most important factors to consider is your retirement benefits, which can significantly impact your financial security during retirement.
Estimating your retirement benefits can be a complex process, but it’s essential to understand the various factors involved. These factors include:
- Age of retirement: Your age at retirement plays a significant role in determining your retirement benefits. The earlier you retire, the lower your benefits may be.
- Years of service: The longer you work, the higher your benefits are likely to be. This is because benefits are typically based on a formula that considers your years of service.
- Average earnings: Your average earnings over a specified period, often the highest-earning years, can influence your retirement benefits. Higher earnings generally result in higher benefits.
- Type of retirement plan: Different types of retirement plans have different benefit structures. For example, traditional pensions provide a fixed monthly income, while 401(k) plans offer tax-advantaged savings opportunities.
To estimate your retirement benefits, you can use the following resources:
- Your employer’s benefits website: Most employers have a dedicated website or portal where you can access information about their retirement plan, including benefit estimates.
- Retirement benefit calculators: There are numerous online calculators available that can provide estimated benefits based on your personal information.
- Financial advisors: A qualified financial advisor can help you understand your retirement benefits and create a comprehensive retirement plan.
It’s important to note that retirement benefit estimates are just projections and may vary depending on factors such as investment performance, legislative changes, and other unforeseen events.
Estimating your retirement benefits is a crucial step in planning for a comfortable and financially secure retirement. By considering the factors involved and utilizing available resources, you can gain a better understanding of your potential income during your golden years.
Factors Affecting Your Benefit Amount
The amount of your Social Security benefit is based on several factors, including your earnings history, your age at retirement, and whether you’re married. Here’s a breakdown of how these factors work.
Earnings History
Your earnings history is the most important factor in determining your Social Security benefit. The Social Security Administration (SSA) calculates your benefit based on your 35 highest-earning years, adjusted for inflation. This means that if you worked for more than 35 years, your lowest-earning years will not be included in the calculation.
Age at Retirement
The age at which you retire also affects your benefit amount. You can start receiving benefits as early as age 62, but your benefit will be reduced. If you wait until your full retirement age (FRA), you’ll receive your full benefit. And if you delay claiming benefits beyond your FRA, you’ll receive an even higher benefit. Your FRA is between ages 66 and 67, depending on your birth year.
Marital Status
Your marital status can also affect your Social Security benefit. If you’re married, you may be eligible for benefits based on your spouse’s earnings record. If you’re divorced, you may be eligible for benefits based on your ex-spouse’s earnings record, as long as you were married for at least 10 years. The amount of your benefit will depend on the age at which you start receiving benefits, as well as your ex-spouse’s benefit amount.
Other Factors
Other factors that can affect your Social Security benefit include:
- Whether you’re disabled
- Whether you’re a survivor of someone who received Social Security benefits
- Whether you’re receiving benefits from another country
Choosing When to Start Collecting Benefits
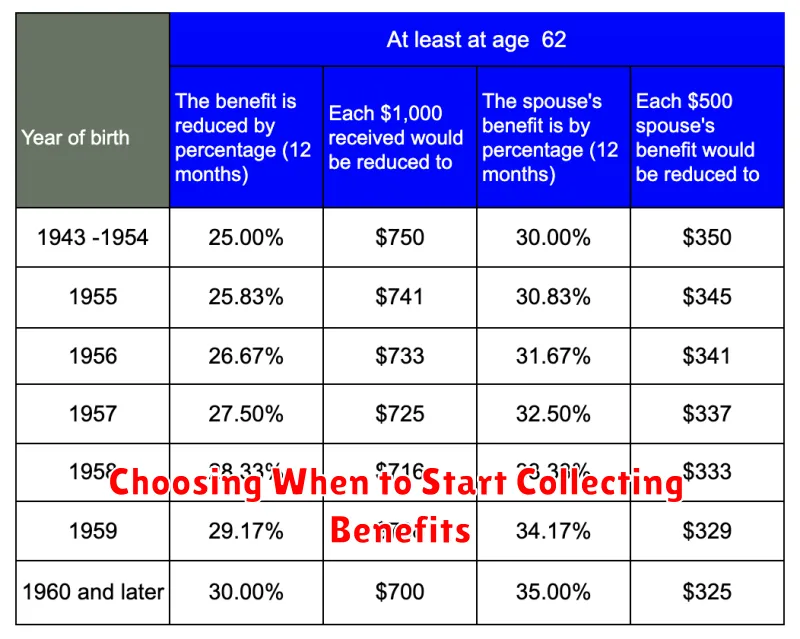
When you reach retirement age, you’ll be faced with a big decision: when to start collecting your Social Security benefits. There are a lot of factors to consider, and the right choice for you will depend on your individual circumstances.
Here are some things to think about:
- Your health: If you’re in good health and expect to live a long life, you may want to wait to start collecting your benefits. The longer you wait, the more you’ll receive each month.
- Your financial situation: If you’re in a tough financial spot, you may need to start collecting your benefits sooner. But if you can afford to wait, you’ll be rewarded with larger monthly payments.
- Your family history: If your family has a history of living long lives, you may want to wait to start collecting your benefits.
- Your current income: If you’re still working and earning a good income, you may want to wait to start collecting your benefits. You can also choose to delay your benefits until age 70, which will give you the highest monthly benefit.
It’s important to do your research and understand the pros and cons of each option before making a decision. You can use the Social Security Administration’s website or consult with a financial advisor to get more information.
Ultimately, the decision of when to start collecting your benefits is a personal one. There’s no right or wrong answer, and what’s best for one person may not be best for another.
Spousal and Survivor Benefits
Social Security benefits are designed to provide financial support to individuals and their families during retirement, disability, or death. Beyond the primary beneficiary, there are benefits available for spouses and survivors.
Spousal Benefits
Spousal benefits are available to the spouse of a Social Security recipient. To be eligible, the spouse must be at least 62 years old, or be caring for a child who is under 16 years old or disabled.
The amount of spousal benefits is determined by the amount of the primary beneficiary’s benefits. The maximum amount of spousal benefits is 50% of the primary beneficiary’s benefits.
It is important to note that a spouse can only receive spousal benefits if they are not eligible for their own higher benefits based on their own work history.
Survivor Benefits
Survivor benefits are available to the surviving spouse, children, and parents of a deceased Social Security recipient. The amount of survivor benefits is based on the deceased individual’s benefits.
The surviving spouse is eligible for benefits at any age if they are caring for a child of the deceased who is under 16 years old or disabled. Otherwise, the spouse must be at least 60 years old to be eligible for survivor benefits.
Unmarried children under the age of 18, or up to 19 if still in high school, are eligible for survivor benefits. Disabled children can receive benefits as long as they remain disabled.
Applying for Spousal and Survivor Benefits
To apply for spousal or survivor benefits, you can contact the Social Security Administration online, by phone, or in person. You will need to provide documentation of your relationship to the deceased individual, such as a marriage certificate or birth certificate.
Taxation of Social Security Benefits
Social Security benefits are a vital source of income for many retirees and disabled individuals. However, a portion of these benefits may be subject to federal income tax. The amount of Social Security benefits that are taxable depends on the individual’s income level and filing status. This article will discuss the rules governing the taxation of Social Security benefits.
How Much of Your Benefits is Taxable?
The amount of Social Security benefits that are taxable is determined by a formula that considers your “provisional income,” which includes:
- Your adjusted gross income (AGI)
- One-half of your Social Security benefits
- Tax-exempt interest income
If your provisional income is below a certain threshold, none of your Social Security benefits will be taxed. However, if your provisional income exceeds this threshold, a portion of your benefits will be taxable. The threshold varies based on your filing status. Here are the thresholds for 2023:
| Filing Status | Threshold |
|---|---|
| Single | $25,000 |
| Married Filing Jointly | $32,000 |
| Head of Household | $25,000 |
| Qualifying Widow(er) | $32,000 |
For example, if you are single and your provisional income is $30,000, then up to 50% of your Social Security benefits could be taxable. The exact percentage of benefits that are taxable is calculated on a sliding scale.
What About State Income Tax?
In addition to federal income tax, some states also tax Social Security benefits. It’s crucial to check your state’s tax laws to determine if your Social Security benefits are subject to state income tax.
Conclusion
It’s important to understand the rules regarding the taxation of Social Security benefits to accurately calculate your tax liability and make informed financial decisions. Remember to consult with a tax professional if you have any questions or concerns about the taxation of your benefits.
Coordinating with Other Retirement Income
Coordinating retirement income from multiple sources can be a complex process, but it’s essential for ensuring a comfortable and financially secure retirement. With careful planning and coordination, you can maximize your retirement income and minimize potential conflicts or gaps in coverage.
Social Security
Social Security is a crucial source of retirement income for many Americans. It’s important to understand your Social Security benefits and how they interact with other retirement income sources. You can use the Social Security Administration website to estimate your benefits and explore various claiming strategies.
Pensions
If you’re fortunate enough to have a pension, it can provide a predictable stream of income throughout retirement. Understand your pension’s payout structure, including any early retirement options or limitations.
Retirement Savings
Your retirement savings, such as 401(k)s and IRAs, provide flexibility in how you withdraw funds during retirement. You can use strategies like Roth conversions or withdrawals to manage taxes and optimize your income. Remember to consider the impact of required minimum distributions (RMDs) for traditional retirement accounts.
Annuities
Annuities can provide guaranteed income streams, which can be helpful in supplementing other retirement income. Explore different types of annuities, including fixed, variable, and indexed, to find the best fit for your needs.
Part-time Work
Many retirees choose to continue working part-time for additional income or simply to stay active. Consider the impact of part-time work on your Social Security benefits and other retirement income sources.
Other Income Sources
Don’t forget about other potential sources of income, such as rental properties, dividends, or royalties. Make sure to factor these into your overall retirement income plan.
Coordination Strategies
Here are some strategies for coordinating your retirement income:
- Maximize Your Social Security Benefits: Research claiming strategies to optimize your benefits.
- Minimize Taxes: Strategically withdraw from retirement savings and other income sources to reduce your tax burden.
- Diversify Your Income Sources: Don’t rely solely on one source of income. Diversification helps mitigate risk and provides flexibility.
- Regularly Review Your Plan: Market conditions and your financial situation can change. Regularly review your retirement income plan to ensure it remains effective.
Professional Advice
It’s highly recommended to consult with a financial advisor who can help you develop a personalized retirement income plan that considers all your needs and objectives. They can also assist with coordinating your income streams and navigating the complexities of retirement planning.
By carefully coordinating your retirement income from multiple sources, you can create a sustainable and secure financial future. Remember that proactive planning and professional guidance are crucial for maximizing your retirement income and achieving your financial goals.

